-
No-code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code AI-native platform to build applications faster
Discover

-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM


-
Industries

- Customers
-
Partners

-
About

What are AI Agents? How AI Enhances Human Work to Boost Productivity
Updated on
July 28, 2025
17 min read
Accelerate Lead Response Time by 61% With Creatio

As workloads continue to grow in complexity and scale, AI agents are emerging as valuable tools for modern professionals. They can automate repetitive tasks, resolve complex challenges, and support smarter, data-driven decision-making. With the AI agent market expected to increase from ~£6.27 ($7.84) billion in 2025 to ~£42.10 ($52.62) billion by 2030, their presence in our daily work is set to accelerate.
This article examines what AI agents are, how they work, and the ways in which they can enhance human capabilities – improving productivity and efficiency.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents – or artificial intelligence agents – are systems capable of acting autonomously, with minimal human intervention, to carry out tasks on behalf of users. Drawing on technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and large language models (LLMs), they are able to analyse data, make decisions, and take actions to complete assigned tasks. It is worth noting that AI agents are not intended to replace humans, but rather to complement their capabilities and enhance operational efficiency – working alongside people and augmenting their abilities.
Autonomous AI agents function independently by sensing an input, reasoning, and selecting the most appropriate response to achieve goals set by human users. More advanced agents can also learn from previous actions and outcomes, allowing them to refine their performance and adapt to evolving conditions and user expectations.
Intelligent agents support users in their daily work by automating routine tasks, surfacing valuable insights, solving complex problems, and enabling seamless interactions with users and other systems.
To understand the foundations of this technology, explore agentic AI
How Do AI Agents Work?
Artificial intelligence agents function through a continuous cycle of sensing, planing, acting, and reflecting – a process that mirrors how humans interpret information and take actions. This approach enables AI agents to comprehend their environment, make informed decisions, and carry out tasks with a degree of autonomy.
The cycle typically involves four key stages:
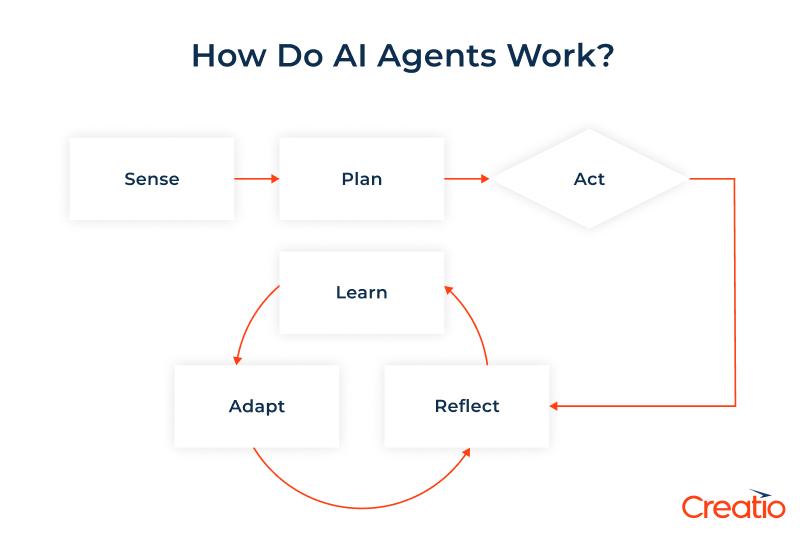
Sense
In the initial stage, the AI agent gathers and interprets information from a range of sources. It utilises a range of tools – including APIs, databases, web scraping, and live data feeds – to access information from both internal and external sources. AI agents are capable of processing text, images, and data, as well as comprehending natural language requests. Additionally, they can also collaborate with other agents to share information, helping to build a more complete picture needed to fulfil their assigned objectives.
Plan
Once the necessary information has been gathered, the AI agent draws on its algorithms, internal models, and knowledge bases to devise a plan of action. At this stage, technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and large language models (LLMs) play a pivotal role:
- ML algorithms enable the agent to recognise patterns, make predictions, and continuously learn from data.
- NLP allows AI agents to interpret and understand natural language – essential for engaging with users, following instructions, and extracting meaning from the text.
- LLMs provide advanced contextual understanding, sophisticated problem-solving capabilities, and generate responses that closely resemble human communication.
Using these algorithms, the AI agent analyses the data it has collected and outlines potential solutions. It breaks down complex problems into manageable steps, determines the required actions along with their sequence, and prepares strategies for addressing possible obstacles. This stage often involves advanced planning, structured problem-solving, and careful risk assessment.
Act
The next stage involves the AI agent putting its plan into action, executing tasks in the appropriate sequence. The specific actions depend on the goal and the context. For instance, the agent may send notifications or emails, update or retrieve records from databases, or conduct real-time data analysis to support informed decision-making. In more complex scenarios, it may perform multiple steps concurrently or collaborate with other AI agents and systems to complete the tasks.
Reflect
A defining feature of advanced AI agents is their ability to reflect, learn and adapt. Once a task has been completed, the agent reviews the results and incorporates user feedback to access whether its actions were effective – and, if not, to identify which aspects did not perform as intended.
To enhance future performance, the AI agent updates its internal models and knowledge base – reinforcing successful strategies and adjusting those that were less effective. This feedback loop, often underpinned by techniques such as reinforcement learning, enables the agent to make better decisions and become increasingly accurate and efficient in meeting its objective over time.
Human in the loop — ensuring oversight and alignment
Although intelligent agents are built to operate autonomously, human oversight remains crucial to ensure they behave as intended. The ‘human-in-the-loop’ (HITL) approach introduces human involvement at key stages, enabling users to monitor, review, and adjust the agent's decisions or actions.
Human intervention plays a pivotal role in enhancing the performance of AI agents, mitigating potential biases, and ensuring alignment with organisational objectives. HITL is particularly critical in industries where AI-driven outcomes carry significant real-world implications – such as healthcare and financial services. This collaborative approach reinforces the principle that, while AI agents are powerful tools designed to extend human capabilities, they are not a substitute for human judgment or emotional intelligence.
Types of AI Agents
There are six types of AI agents, each differing in complexity, memory capacity, and decision-making ability. These fundamental distinctions influence how agents behave and define the range of tasks they are suited to within business environments.
Outlined below are the most common types of AI agents, ranked from the simplest to the most advanced:
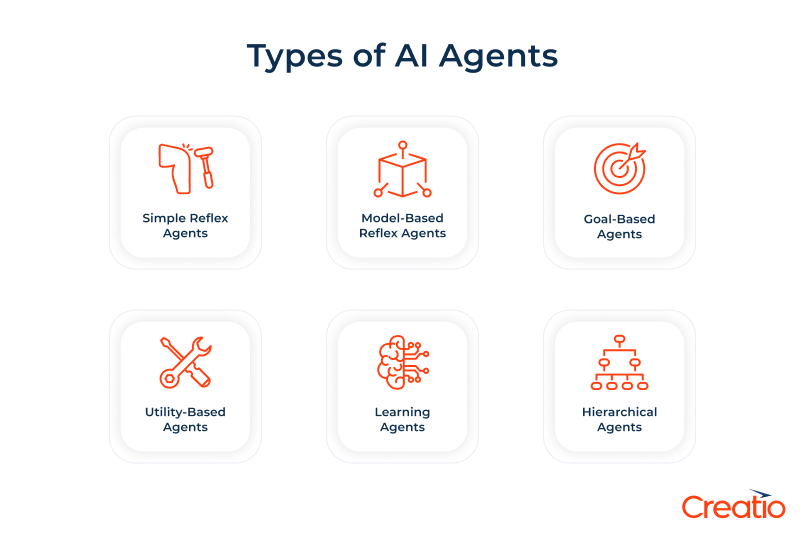
1. Simple Reflex Agents
- How they work: these are the most basic types of AI agents, designed to carry out simple tasks. They operate according to a set of predefined rules, executing pre-programmed actions whenever particular conditions are met. Simple reflex agents assess only the current state of the environment – they have no memory of past events and do not consider future consequences. As such, they cannot evaluate their performance or adapt to situations outside their programmed scenarios and rules.
- How they support humans: simple reflex agents are ideal for automating repetitive, routine tasks within predictable environments. By handling these low-level actions, they help reduce the burden of administrative work and free up time for humans to focus on more complex decision-making.
- Example: when a new contact is added to a marketing list, a simple reflex agent automatically sends a “Welcome” email.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
- How they work: unlike simple reflex agents, model-based agents use both their current perception and memory to construct an internal model of the environment. This model reflects the current state of the world and how it is likely to evolve over time, enabling the agent to take past experiences and potential future outcomes into account when making decisions. The internal model is continuously updated as new information becomes available.
- How they support humans: model-based reflex agents are capable of assisting with more complex tasks, particularly in dynamic environments. Their ability to adapt to changing conditions allows them to support better-informed decisions and respond appropriately to evolving circumstances.
- Example: an AI agent monitors stock levels, forecasts future demand, and automatically places orders for new supplies when needed.
3. Goal-Based Agents
- How they work: these agents are designed to achieve specific objectives. Unlike reflex agents, which respond to immediate inputs, goal-based agents evaluate various options and determine the most effective course of action to reach a defined goal.
- How they support humans: goal-based agents are particularly useful when the end result is clearly defined. They do not require detailed instructions or rigid rules to carry out a task.
- Example: an AI agent oversees the invoice process, verifying that all required data and authorisations are in place before marking it as approved.
4. Utility-Based Agents
- How they work: utility-based agents represent the most sophisticated type of rational agent. They go beyond simply achieving a goal by evaluating potential actions based on how effectively they fulfil the objective. In doing so, they take into account factors such as efficiency, cost, risk, and overall benefit. The agents select the option that is likely to deliver the most favourable outcome.
- How they support humans: utility-based agents are valuable in complex decision-making processes, where multiple factors must be considered. They assess a range of possible actions and recommend those that are most likely to optimise results.
- Example: an AI agent routes incoming support tickets to the most appropriate team member by analysing the nature of the complaint, the agent's expertise, current queue lengths, and the urgency of the issue – balancing both customer satisfaction and agent workload.
5. Learning Agents
- How they work: Learning agents develop and improve over time by analysing past experiences and external feedback. Typically, they comprise a learning component that updates the agent’s behaviour, a critic that assesses its performance, and a problem generator that suggests new actions for exploration.
- How they support humans: learning agents adapt to evolving conditions and user behaviour without the need for reprogramming. By continuously refining how tasks are carried out, they help streamline business processes and reduce the need for manual intervention or frequent adjustments.
- Example: an AI agent continually learns which lead behaviours – such as specific web pages visited or email engagement rates – are the strongest predictors of successful conversions, and automatically updates its lead scoring model accordingly.
6. Hierarchical agents
- How they work: these advanced agents are advanced systems structured in layers. A high-level agent interprets the user’s goal, breaks it into smaller, manageable tasks, and assigns these to lower-level agents responsible for carrying them out.
- How they support humans: hierarchical agents are particularly effective in managing complex tasks and coordinating large-scale business processes involving multiple stages or functions.
- Example: a group of AI agents manages the entire customer lifecycle. The top-level agent oversees the full journey, while specialised agents handle acquisition, onboarding, retention, and re-engagement.
Advantages of AI Agents
Integrating AI agents into business operations offers a range of advantages – from improved productivity to more informed decision-making.
Below are some of the key benefits AI agents can deliver:
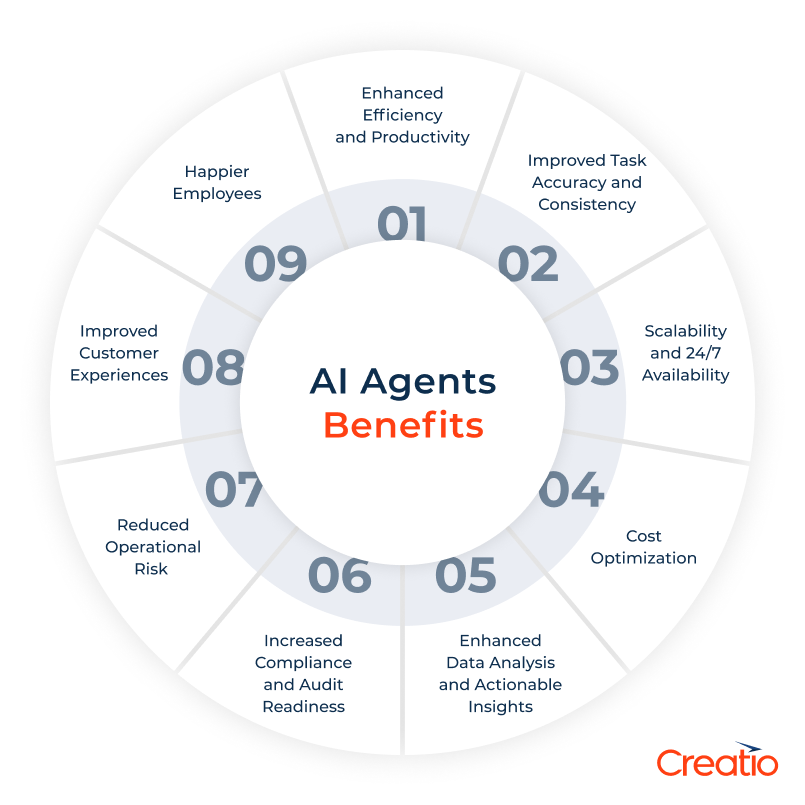
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity: AI agents can automate repetitive and mundane tasks that traditionally consume plenty of employees' time. Tasks such as data entry, responding to standard enquiries, assigning leads, or generating regular reports can be handled by AI agents, allowing staff to concentrate on more strategic, complex, and creative work that relies on distinctly human capabilities.
- Improved task accuracy and consistency: AI agents are designed to follow instructions precisely and apply rules consistently, helping to minimise manual errors in data entry, transaction processing, and routine decision-making. While not infallible, AI agents contribute to greater accuracy and reliability across repetitive processes.
- Scalability and round-the-clock availability: unlike human workers, AI agents do not require rest and can operate continuously, 24 hours a day. This enables businesses to scale their operations in response to increased demand without the need to hire additional staff. With autonomous agents in place, businesses can maintain uninterrupted, high-quality service and support – even outside standard working hours.
- Cost optimisation: by automating tasks, enhancing efficiency, and reducing the likelihood of errors, AI agents contribute to lower operational expenses. This includes savings on labour, avoiding expense errors, and making more effective use of resources through improved allocation.
- Enhanced data analysis and actionable insights: intelligent agents can process and analyse large amounts of data far more quickly than traditional systems – and significantly faster than any human analyst. This enables them to identify patterns and trends, and to highlight actionable insights, supporting better-informed decisions in areas such as planning, forecasting, and problem-solving.
- Increased compliance and audit readiness: by adhering strictly to predefined workflows and rules, AI agents help ensure regulatory procedures are carried out consistently. In addition, they generate detailed logs and audit trails, making it easier for organisations to demonstrate compliance.
- Reduced operational risk: through standardisation, automation, and continuous monitoring, AI agents help mitigate the risk of human error, process deviations, and delays – particularly in mission-critical operations such as payments, approvals, and onboarding.
- Improved customer experiences: AI agents can enhance customer service professionals by delivering instant responses to routine queries and directing more complex issues to the appropriate human agent – complete with full context. This streamlines resolution times, enables more personalised interactions, and ultimately improves overall customer experience.
- Happier employees: by taking on the repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI agents free up employees to focus on higher-value activities – such as building relationships, innovating, and shaping strategy. This shift not only increases productivity but also contributes to greater job satisfaction.
Real-World Use Cases for AI Agents
AI agents are already playing a role across many areas of the digital landscape, often operating behind the scenes to boost efficiency, enhance user experience, and support more informed decision-making. According to Forbes, by the end of 2025, one in four companies will be running pilot programs powered by AI agents. That figure is expected to double by 2027, reflecting a rapid shift from experimentation to widespread adoption. This trend highlights the expanding influence of AI agents in driving transformation and shaping competitive advantage.
The following real-world examples illustrate how organisations can effectively deploy AI agents across various business contexts:
Intelligent Lead Scoring and Routing
An AI agent continuously monitors incoming leads from all channels – including the website, social media, and digital event such as webinars or product launches. It analyses prospect’ data (e.g. company size, industry, on-site behaviour, and previous interactions) against predefined ideal customer profiles to generate a qualification score. Based on this score, the agent automatically routes high-potential leads to the most suitable sales representative, provides a summary of key information, and recommends the next best action – helping to accelerate the sales and improve conversion rates.
Find out more about how AI sales agents augment sales representatives’ work
Customer Support Automation
AI agents can be deployed as intelligent chatbots or virtual assistants to manage incoming customer enquiries. These agents are capable of handling frequently asked questions, resolving basic issues, and carrying out simple tasks on behalf of customers – such as checking order status or completing a return form. By integrating AI agents in the customer support operations, businesses can significantly reduce response times and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Marketing Campaign Automation and Optimisation
AI agents integrated into marketing platforms can automatically segment audiences, personalise content based on customer needs, and trigger multi-step email campaigns in response to user behaviour. For instance, an autonomous agent might initiate a sequence of follow-up emails after a webinar registration, or adjust the advertising budgets in real time based on campaign performance.
In addition, an AI agent can help maximise conversion rates by continuously analysing performance metrics – such as open rates and click-through rates – and optimising campaigns accordingly. To improve results, the agent may autonomously refine specific elements, such as email subject lines or ad creatives, and conduct A/B testing to identify the most effective version.
Intelligent Meeting Scheduling
AI agents can schedule meetings with clients by coordinating across multiple calendars, user preferences, and time zones. They identify optimal time slots for all participants, automatically send invitations, update calendars, and reschedule meetings when necessary. In addition, AI agents can update customer management system (CRM) records with meeting details and outcomes, providing a valuable summary.
Dynamic Product Recommendation
E-commerce businesses can deploy autonomous AI agents to automatically generate and display personalised product recommendations based on each customers’ shopping baskets, browsing behaviour, and online activity. Moreover, AI agents continuously collect new data and update their suggestions in real time to reflect current customer preferences and needs.
Sales representatives can also leverage insights provided by AI agents to tailor offers to individual clients, delivering more personalised cross- and up-selling recommendations that help increase deal value.
Knowledge Retrieval
When a sales representative or customer service agent needs quick access to specific product details, customer account information, policy documents, or similar resources during a call or a meeting, an AI agent can retrieve and present this information instantly. Integrated with the organisation’s CRM and knowledge base, AI agents act as real-time assistants – locating relevant data, generating concise summaries, and even suggesting the most appropriate response to support efficient and informed interactions.
Industry-specific AI agents
According to research by Markets and Markets, the market for industry-specific AI agents is expected to grow by over 35% in the next five years. This growth includes agents designed for specific functions within sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and legal services – often integrated directly into industry-specific software and workflows.
Below are a few examples of tasks that industry-specific AI agents can perform:
- Healthcare: AI agents help healthcare professionals by automatically scheduling patient appointments, updating medical records, and processing insurance claims.
- Finance: financial institutions use AI agents to automate fraud detection, credit scoring, and regulatory compliance checks.
- Manufacturing: AI agents can monitor equipment performance, manage inventory, and optimise supply chains.
Challenges of Using AI Agents
While AI agents offer significant potential for transforming business operations, their implementation and ongoing management can present a number of challenges.
Below are some of the most common issues – along with recommended solutions:
Challenge | Solution |
| Access to high-quality data | Establish robust data governance frameworks and use automated tools for data validation and cleansing. |
| Complex implementation and integration | Opt for a vendor (e.g., Creatio) that offers native AI agents integration to accelerate time to value. |
| Ethical concerns and bias | Implement strong governance policies and responsible AI practices throughout development and review. |
| Lack of transparency | Select AI agents that provide clear visibility into how decision are made on and on what basis. |
| Security and privacy risks | Find a vendor that offers robust security protocols and ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations. |
- Access to high-quality data: AI agents are only as effective as the data they rely on. Incomplete, outdated, or biased datasets can result in inaccurate results, errors, and poor decision-making. Businesses should ensure that their agents have access to high-quality, relevant, and comprehensive data in order to operate reliably.
- Complex implementation and integration: Deploying agents often requires specialized expertise in machine learning and AI system design. Tailoring agents to meet specific business requirements – and integrating them with legacy systems, CRMs and internal tools – can present significant challenges. A practical solution is to select a vendor, such as Creatio, that offers native AI agents integration within their system, thereby significantly accelerating time to value.
- Ethical concerns and bias: AI agents learn from the data they are trained on. If that data reflects existing societal or historical biases, the agent may accidentally replicate – or even reinforce – those biases in its decision-making (for example, in lending assessments or recruitment recommendations). To mitigate this risk, businesses should embed strong governance frameworks and responsible AI practices into both the development and review processes.
- Lack of transparency (the ‘black box’ problem): Many advanced AI models, particularly those built on deep learning algorithms, can operate as ‘black boxes’, making it difficult to trace or explain how decisions are reached. This opacity can undermine trust and pose compliance risks, especially in regulated industries. To address this challenge, businesses should carefully assess available AI agents and prioritise those that offer the maximum of transparency.
- Security and privacy risks: As AI agents process large volume of sensitive business and customer data, they can become potential targets for cyber threats. To safeguard this information and maintain customer trust, businesses should work with AI providers that offer robust security measures – including data encryption, secure access controls, and adherence to strict data protection regulations such as UK GDPR and CCPA.
Creatio’s AI Agents — Enhancing Human Capabilities Through Role-Based Intelligence
Creatio is an AI-native platform for automating CRM and workflow processes using a no-code approach. At its core is Creatio.ai – a powerful AI assistant that delivers a unified AI architecture supported by a robust set of cutting-edge capabilities. Creatio seamlessly integrates all key AI patterns, including predictive, agentic, and generative AI, enabling businesses to eliminate operational inefficiencies, enhance smarter decision-making, and achieve significant productivity improvements.
With Creatio.ai, business users collaborate directly with AI agents, unlocking the full potential of human and digital talent working in harmony. AI agents bring new levels of speed and agility, allowing teams to work more efficiently, concentrate on creativity, and deliver unprecedented results.
Watch this video to discover how Creatio’s actionable AI approach works:
AI agents automate routine work and provide real-time recommendations, enabling users to dedicate more time to engaging with customers and focusing on strategic tasks. They autonomously deliver contextual insights, help prioritise daily tasks, and offer hands-on support through the working day. Moreover, Creatio’s AI agents are embedded within familiar productivity tools – such as Microsoft Outlook and Teams – surfacing key information at the right moment to boost overall productivity.
Creatio’s role-based AI agents are designed for specific jobs within sales, marketing, and customer service departments:
- Sales teams can benefit from the Sale Agent, which automates preparation, personalises outreach, and helps close deals faster by intelligently anticipating customer needs and recommending next-best actions. They can also deploy role-based AI agents, such as an Account Research Agent, a Meeting Agent, and a Quote Generation Agent.
- Marketing teams can leverage the Marketing Agent to scale content creation and campaign execution. Role-based agents available for marketers include the Marketing Content Agent, Email Generation Agent, and Lead Conversion Agent.
- Service teams using the Service Agent can resolve queries more quickly and accurately by leveraging AI to extract insights, suggest actions, and streamline communication across channels. Customer service agents can also collaborate with role-based agents, including the Customer Support Agent and Knowledge Base Agent.
In addition, business users can create new agents using the No-Code Agent Builder, visually combining skills, workflows, and knowledge – all without requiring technical expertise. This innovative feature combines no-code technology with advanced AI capabilities, empowering non-technical users to design intelligent digital teammates tailored to their unique needs and tasks.
Find out more about how Creatio.ai can support your customer-facing teams
Creatio.ai is built with security, transparency, and responsible AI at its core. It provides enterprise-grade data privacy and security features, meeting the highest standards of privacy and compliance. By incorporating a human-in-the-loop approach, Creatio.ai ensures that AI decisions are guided by human oversight, enhancing accountability and trust.
What Sets Creatio Apart From Other Vendors?
While many vendors position their AI agents as replacements for human workers, suggesting they will take over entire roles, Creatio adopts a fundamentally different approach. Rather than replacing people, Creatio’s AI agents are designed to act as digital teammates – augmenting human intelligence.
At Creatio, we believe the true power of AI lies in collaboration. Our AI agents are designed to work alongside individuals and teams, supporting them in automating repetitive tasks, providing intelligent recommendations, and enabling faster, more informed decisions. This human-centric philosophy fosters trust, transparency, and broader adoption. It ensures that users feel empowered rather than displaced, and are more likely to embrace AI-powered tools.
Unlike many vendors that treat AI as a premium add-on, Creatio includes these innovations as part of its core – with no additional licences, no hidden fees, and no complex integrations. This approach ensures every organisation can achieve wide-scale AI adoption across teams, without barriers or complications.

While others are still offering fragmented AI products and complex pricing models, we’ve taken a different path. We offer one platform, one experience, and one clear route to accelerated AI adoption and realizing real business value.
In a market where others may promise automation at the cost of human roles, Creatio stands out by delivering responsible innovation – enhancing efficiency, supporting creativity, and valuing human expertise.
Want to learn how Creatio.ai can support your business?


