-
No-code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code AI-native platform to build applications faster
Discover

-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM


-
Industries

- Customers
-
Partners

-
About

AI Agents in the Financial Sector: Use Cases, Business Value and Emerging Opportunities
Updated on
September 26, 2025
14 min read
Enhance Business Operations with Creatio’s AI Agents for FinServ

The financial sector remains at the forefront of adopting advanced AI technologies, supporting financial professionals in areas such as fraud detection, risk assessment, decision-making and forecasting. The increasing integration of these tools is clearly reflected in broader market trends. According to Markets and Markets, the global AI in finance market is expected to grow from $38.36 billion (~£28 billion) in 2024 to a remarkable $190.33 billion (~£142 billion) by 2030.
One of the principal drivers of the growth is the rise of AI agents – intelligent, autonomous systems capable of processing vast volumes of financial data, identifying patterns, and making complex decisions with minimal human involvement. For financial institutions, these agents facilitate a shift from reactive analysis to proactive, real-time actions, improving efficiency at scale without raising operational expenses.
This article explores the evolving role of AI agents in the financial industry, outlining their capabilities, underlying mechanisms, and the strategic value they offer. It further addresses typical use cases, critical considerations for adoption, and the means by which an AI-native infrastructure enables teams to embed intelligence into routine financial processes.
Understanding AI Agents in Finance
AI agents designed for financial services are intelligent, autonomous systems capable of executing sophisticated financial tasks with little to no human involvement. They are driven by technologies such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and advanced data analytics. By automating routine and complex workflows, AI agents enhance speed, accuracy, and operational scalability across finance functions.
In contrast to Generative AI systems that merely respond to user requests, AI agents are designed to pursue goals. They learn continuously, adjust to new trends in data, and act in response to the context. Essentially, they function as proactive digital assistants for finance teams – capable of interesting instructions, processing large volumes of data, making informed decisions, and independently managing routine and complex tasks.
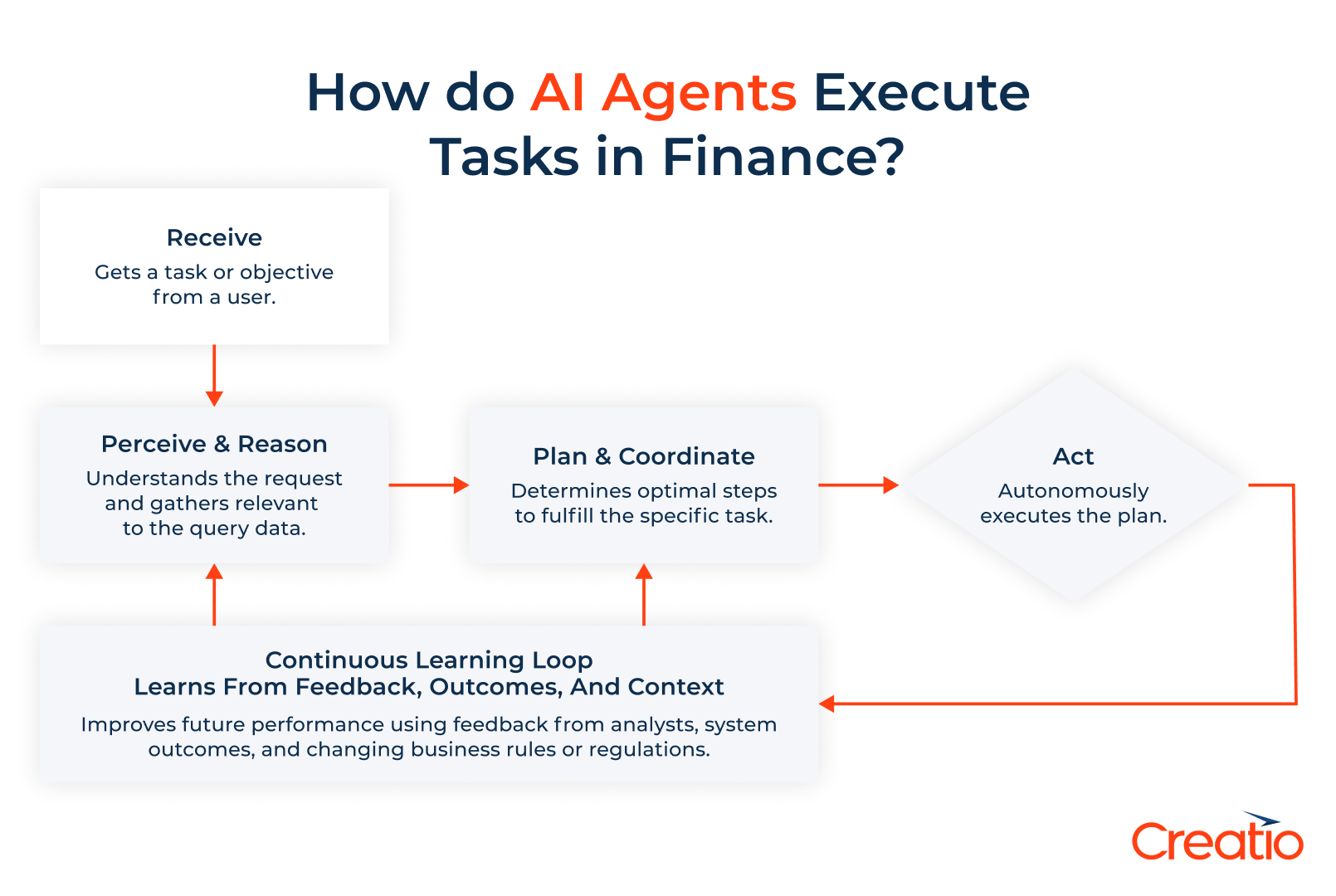
AI agents are increasingly employed by financial institutions to manage data-heavy processes and support real-time decision-making. For instance, finance-focused AI agents are capable of:
- Flagging anomalies or suspicious behaviour in loan applications
- Assessing creditworthiness through the analysis of historical and live market data
- Generating regulatory compliance reports
- Delivering tailored personalised financial insights in real time
AI agents can operate independently or via intuitive interfaces, enabling finance teams to work more efficiently, reduce the likelihood of human error, and maintain focus on higher-level strategic tasks. With continued adoption, the role of AI agents is expected to grow within the financial sector, extending from supporting individual investors and finance teams to fostering innovation across the industry.
Principal Advantages of AI Agents in the Financial Sector
AI agents provide a range of advantages for financial institutions aiming to modernise operations, reduce expenses, and enhance customer engagement. The following section highlights the most impactful benefits these systems bring to the evolving financial landscape.
Enhanced Operations at Scale
A major advantage of AI agents is the ability to automate routine, time-consuming workflows. Activities including data entry, validation, compliance checks, and reporting workflows, once reliant on manual intervention, can be executed independently by AI systems. As a result, financial institutions are able to scale operations capacity efficiently, without a corresponding rise in expenditure or staffing.
Automation help reduce human error, ensuring that day-to-day operations run more efficiently. Freed from repetitive administrative tasks, finance professionals can devote mote time to higher-value tasks, such as client guidance or developing financial strategies.
Smarter, Autonomous Decision-Making
By processing extensive amounts of structured and unstructured data in real time, AI agents introduce both speed and rigour to data analysis, uncovering contextual insights of genuine value. This empowers finance professionals to implement AI decision-making processes that are not only more efficient but also deliver impressive outcomes.
For instance, BlackRock uses custom-built AI systems to support its investment strategy, analysing market trends, sentiment, and a range of financial data to identify actionable investment opportunities. These AI systems enhance portfolio decisions on a scale and at speed far beyond the capabilities of human analysis alone.
Robust Risk Management
Risk management remains a fundamental pillar of the financial sector. Through continuous monitoring, AI agents enhance this functions by identifying anomalies, uncovering irregular patters, and flagging potential threats before they escalate. Operating in real time, such systems assist financial institutions in detecting fraud, refining risk assessments, and limiting exposure across vital operations areas.
Furthermore, the adaptability of AI agents, driven by their ability to learn from evolving data and operate at scale, enhances the precision of detection systems and bolster their resistance to evolving forms of fraud.
Personalised Customer Experience
AI agents facilitate the delivery of faster, more personalised service at scale, thereby enhancing relationships between financial institutions and their customers. Through the analysis of customer goals and financial data, these systems are able to generate recommendations specifically aligned with client’s requirements. They also provide proactive support and round-the-clock availability via digital self-service tools, which enable the automation of day-to-day processes such as budgeting, spending insights, and personalised financial guidance.
Reinforced Compliance and Security
With financial regulations constantly shifting, institutions face ongoing challenges in keeping pace with policy changes. AI agents do more than assist teams in meeting regulatory requirements, they integrate compliance directly into operational workflows, helping to ensure accountability and security across the organisation.
For instance, these AI agents are capable of:
- Detecting suspicious activity linked to money laundering or fraud
- Automatically updating rules in line with evolving policies
- Producing audit-ready reports to simplify regulatory reporting
- Applying compliance standards consistently across systems, teams, and workflows
By transforming compliance into a continuous and automated process, financial institutions can reduce the risk of human error, ease the burden of audits, and remain aligned with constantly evolving regulatory requirements.
Increased Revenue and Cost Optimisation
Through the automation of repetitive tasks and workflows, AI agents help to eliminate operational inefficiencies while unlocking new opportunities for revenue generation. Processes such as underwriting, compliance reporting, and customer onboarding are executed with greater speed and precision, resulting in optimised workloads and fewer manual errors. This, in turn, enables teams to concentrate on more strategic initiatives.
According to a recent survey by NVIDIA, over 60% of organisations reported that AI had helped reduce annual costs by 5% or more – a compelling demonstration of its financial impact.
In terms of revenue generation, AI-driven insights enable more strategic cross-selling, refined pricing models, and highly personalised product offerings. By analysing customer data and behavioural patterns, AI agents can suggest the most relevant product at the optimal time, thereby enhancing conversion rates with minimal manual effort.
The World Economic Forum resent report, “AI in Financial Services”, reveals that 70% of financial services executives expect AI to play a significant role in driving revenue growth over the next few years.

High-Impact Use Cases of AI Agents in Financial Sector
In 2023, financial services companies invested over $35 billion in AI. This figure is projected to reach $97 billion by 2027, particularly within core industry segments such as banking, insurance, and credit unions. A rising share of that investment is now being channelled into AI agents, as institutions seek to embed them within critical, high-value processes.
Outlined below are the key ways in which these AI systems are currently transforming the financial sector:
1. Credit Assessment and Loan Origination
AI agents bring significant improvement to traditional manual, document-intensive workflows that often delay credit evaluation and loan origination. By automating essential steps such as gathering applicant data, verifying documents, and performing real-time risk assessments, they help to ensure greater consistency and accuracy throughout the process.
For instance, rather than reviewing each case manually, credit teams now leverage AI to manage routine assessments, allowing them to concentrate on more complex cases or high-value clients.
2. Compliance and Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding within the financial sector is a compliance-intensive process that demands speed, precision, and alignment with ever-evolving financial regulatory standards. AI agents support these needs by automating tasks such as identity verification (KYC), documents scanning, and customer data cross-checks against AML watchlists and policy rules.
By streamlining these business operations through AI, compliance teams are able to concentrate their attention precisely where it matters most – on flagged exceptions or potential risk indicators. As a result, companies can accelerate onboarding, scale the workflows with greater efficiency, and perform tasks in strict adherence to regulatory standards, all whilst maintaining a smooth and professional experience for the customer.
3. Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI agents support the financial industry in the prevention of fraud by continuously monitoring transactions, user behaviour, and system activity in real time. These systems can detect suspicious patterns, such as unusual spending, login anomalies, or questionable credentials, far more effectively than traditional AI models and rule-based engines.
Consider a real-world scenario: when AI agents detect unusual activity – such as login anomalies or suspicious spending patterns – they may initiate additional verification or temporarily pause the transaction for review by a human analyst. This real-time oversight plays a vital role in preventing losses and reinforcing client trust.
4. Customer Experience and Engagement
Financial institutions are increasingly using AI agents to deliver personalised customer experiences at scale, thereby enhancing the responsiveness, accessibility, and relevance of the services. For instance, AI-driven digital assistants support customers in opening accounts, monitoring financial objectives, and receiving product recommendations aligned with their income levels, spending patterns, or risk profiles.
Within sales and marketing functions, AI agents analyse customer behaviour to identify potential upsell opportunities. Real-world examples include recommending a premium credit card to a customer demonstrating increased transaction activity, or proposing a mortgage refinancing option in response to market shifts. In addition, AI systems support lead scoring, craft tailored communication, and automate follow-ups, empowering financial professionals to engage clients more effectively and prioritise the most valuable interactions.
5. Risk-Based Pricing and Underwriting
Through the analysis of extensive risk-related data, including credit history, market trends, and behavioural patterns, AI agents are able to enhance the precision of pricing and the efficiency of underwriting. They can automatically calculate risk scores, recommend suitable pricing tiers, and escalate anomalies for assessment by human analysts.
AI-driven insights are increasingly supporting underwriting teams in making timely and more consistent decisions. For instance, AI agents may identify subtle risk indicators that a human underwriter could miss, or evaluate how different pricing strategies affect profitability. This leads to faster decision-making, more equitable pricing, and stronger alignment with each client’s risk profile.
6. Trading and Portfolio Optimisation
A further illustration of AI agents role within the financial sector lies in their ability to enhance the operational efficiency of trading teams and portfolio managers. Through the analysis of real-time market volatility, economic indicators, and relevant news, these systems are able to flag potential risks, uncover opportunities, and recommend timely portfolio adjustments.
AI agents play a significant role on trading desks by evaluating earnings reports, market fluctuations, and other relevant data to provide actionable insights. Portfolio managers may then adjust strategies accordingly or delegate trade execution to the agents, within established parameters.
7. Automated Compliance Processes
Beyond onboarding, AI agents continue to support ongoing compliance by monitoring transactions, applying regulatory rules across departments, and validating documentation in real time. In doing so, they reduce audit risk and enables teams to concentrate on more strategic aspects of governance.
As an illustration, AI agents are capable of identifying patterns indicative of potential money laundering (AML), confirming that documentation adheres to evolving regulatory requirements, and automatically generating compliance reports to support alignment with industry regulations.
Principal Challenges of AI Agent Integration
The integration of AI agents, as with any emerging technology, brings a range of challenges. Initial barriers – including limited financial resources – are gradually fading, with 50% fewer organisations reporting cost constraints, according to Nvidia’s “State of AI in Financial Services” report. However, as AI adoption moves from experimentation to large-scale implementation, new complexities are likely to arise.
The adoption of AI agents in the financial services sector is accompanied by several key challenges, outlined below:
- Data Privacy and Security. In the financial services industry, AI agents process critically sensitive data, including customer information, regulatory records, and transaction details. Adhering to rigorous data protection laws, cybersecurity standards, and compliance frameworks – such as UK GDPR and PCI DSS – is not optional, but a continuous and fundamental requirement.
- Data Quality and Accessibility. When data is siloed, incomplete, or inconsistent, it undermines the accuracy of AI, particularly in critical areas such as lending, fraud detection, and asset management.
- Integration with Legacy Systems. A significant number of financial institutions still operate on ageing, legacy infrastructure. Ensuring AI agents can connect with core financial tools, CRMs, and compliance platforms, while maintaining established workflows – remains a complex challenge, both technically and strategically, for today’s organisations.
- Oversight and Human-in-the-Loop Design. In highly regulated sectors as financial services, AI agents must function under appropriate human oversight. Achieving the appropriate balance between autonomous decision-making and manual control is essential to maintaining trust, accountability, and regulatory compliance.
- Regulatory and Compliance Complexity. As with many financial technologies, AI agents must be both explainable and auditable. The ever-evolving landscape of global and regional regulations introduces an added layer of complexity to their deployment and scale.
- Lack of AI literacy. A lack of internal AI expertise can significantly slow the integration of AI agents in financial services. Fostering AI literacy across business and technical functions is essential to unlocking its full potential in the long term.
As these challenges illustrate, implementing AI agents within the financial sector demands more than advanced technology alone – it requires a clear, strategic approach aligned with the organisation’s specific objective and requirements.
To support you in leading this transformation, we’ve developed the No-Code Playbook: Age of AI (2nd Edition) – a 200-page, vendor-agnostic guide designed to help teams build and scale complex business applications utilising no-code. This new edition has been enhanced for the AI era, demonstrating how to extend no-code success through AI agents, automation, powerful tools and modern development approaches. It also offers new insights, updated frameworks, and practical recommendations to help organisations harness the potential of AI, while ensuring human oversight remains at the core.
No-code Playbook
Discover how to build complex business applications effortlessly – get your free 200-page No-Code Playbook today!

The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Finance
AI is poised to become ever more integral to the financial services sector in the years to come. As adoption scales and technologies continue to mature, current limitations – such as fragmented data, system bottlenecks, and narrow AI use cases – will likely give way to more intelligent, agile, and industry-aligned solutions.
The World Economic Forum’s report on Artificial Intelligence in Financial Services outlines several financial trends that are expected to define the future landscape:
- Maturation of AI Agents. AI agents in the financial sector are set to evolve from task-specific assistants to autonomous, multi-functional systems with the capacity to execute complex, end-to-end functions. In the future, AI agents will be deployed across a broader range of challenges and decision-making scenarios, ultimately transforming the way financial services operate.
- Small language models (SLMs). In contrast to large, general-purpose models, SLMs are designed for high efficiency and task-specific precision. Within the financial sector, these intelligent systems are well-suited to handling domain-specific, repetitive tasks – such as responding to customer inquiries regarding particular financial products or policies – more swiftly and with fewer resources than traditional LLMs.
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This approach enhances generative AI by incorporating to real-time, relevant information from external sources such as knowledge base or databases. As a result, the accuracy and reliability of AI-generated responses are significantly improved. For financial services, RAG is particularly valuable in helping AI agents minimise hallucinations and support compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Quantum Computing. The fusion of quantum computing and AI holds presents immense potential for the financial services sector, particularly in areas that demand advanced pattern recognition. As the technology continues to mature, financial institutions will be able to significantly accelerate traditional problem-solving processes. For instance, they could enhance fraud detection across large volumes of transactional data, improve credit risk modelling, optimise asset allocation, and much more.
- Responsible AI. As AI becomes more deeply embedded in high-stakes sectors such as finance, the adoption of responsible AI practices will be essential –not only to drive efficiency, but also to ensure transparency, fairness, and compliance with evolving regulatory standards across all AI-driven operations.
Creatio AI for Finance: Enhance Your Unique Operations with AI-Powered Automation
AI adoption within financial services often begins with a collection of specialised tools – one for fraud detection, another for customer service, and separate solutions for compliance, onboarding, reporting, and beyond. However, as the number of AI use cases expands, this fragmented approach can result in escalating costs, duplicated efforts, and disconnected teams.
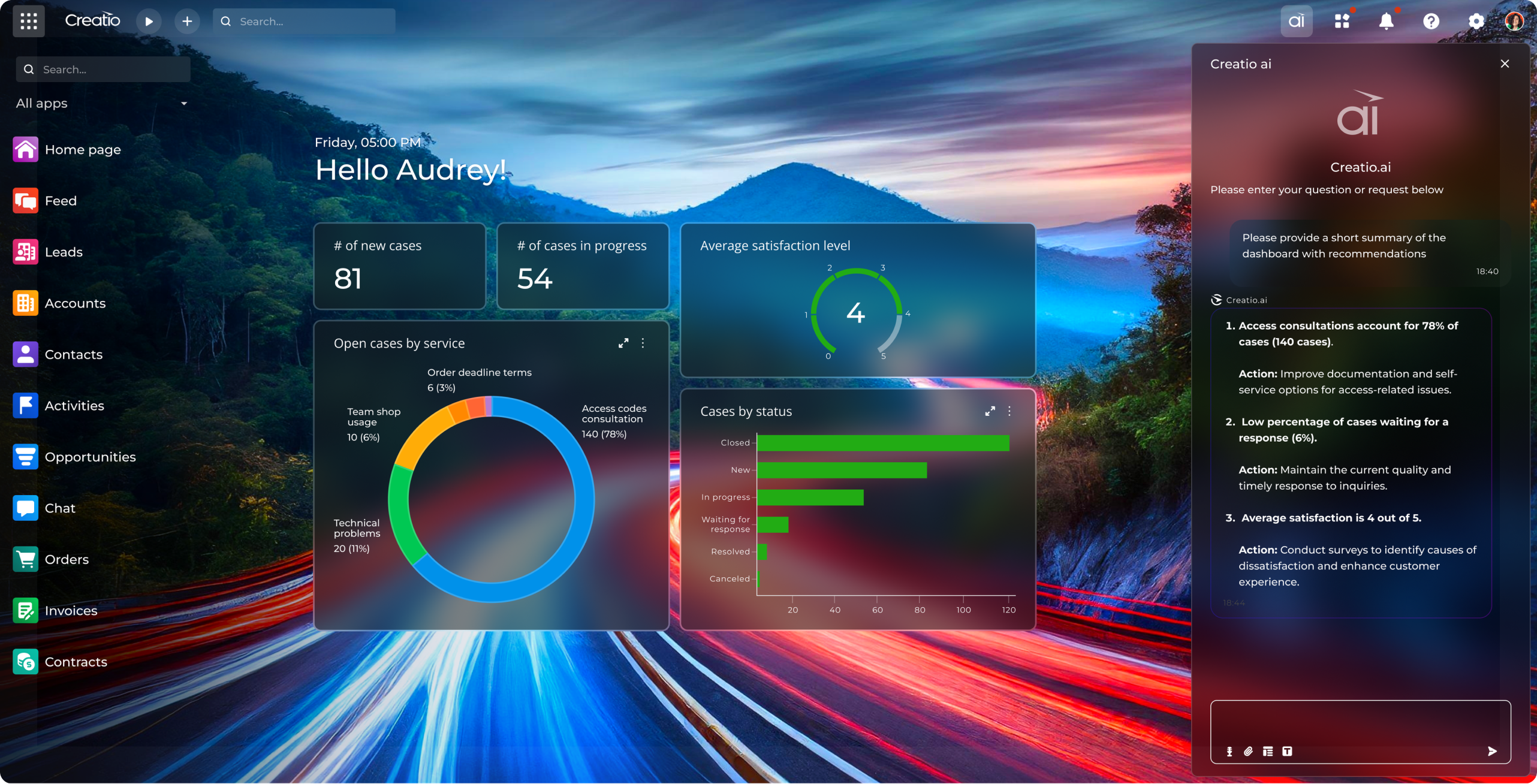
To deploy AI agents effectively – at scale, with agility, and without the need for extensive coding – financial institutions require a comprehensive, AI-native platform that aligns with their specific business processes. This is precisely where Creatio delivers value.
Creatio is a unified no-code platform that enables financial organisations to automate business workflows and CRM through advanced AI capabilities. Unlike traditional financial service tools, Creatio enables users to orchestrate end-to-end workflows across front-, middle-, and back-office functions, eliminating fragmentation and fostering seamless collaboration across business teams.
The platform allows financial institutions to design, launch, and manage FinServ AI agents from a single environment, supporting a wide range of use cases – from credit scoring, customer onboarding, and service requests to underwriting, fraud prevention, KYC/AML compliance. With composable architecture and no-code agility, Creatio enables financial teams to implement and scale AI across core business workflows – more rapidly, intelligent, and with complete control.
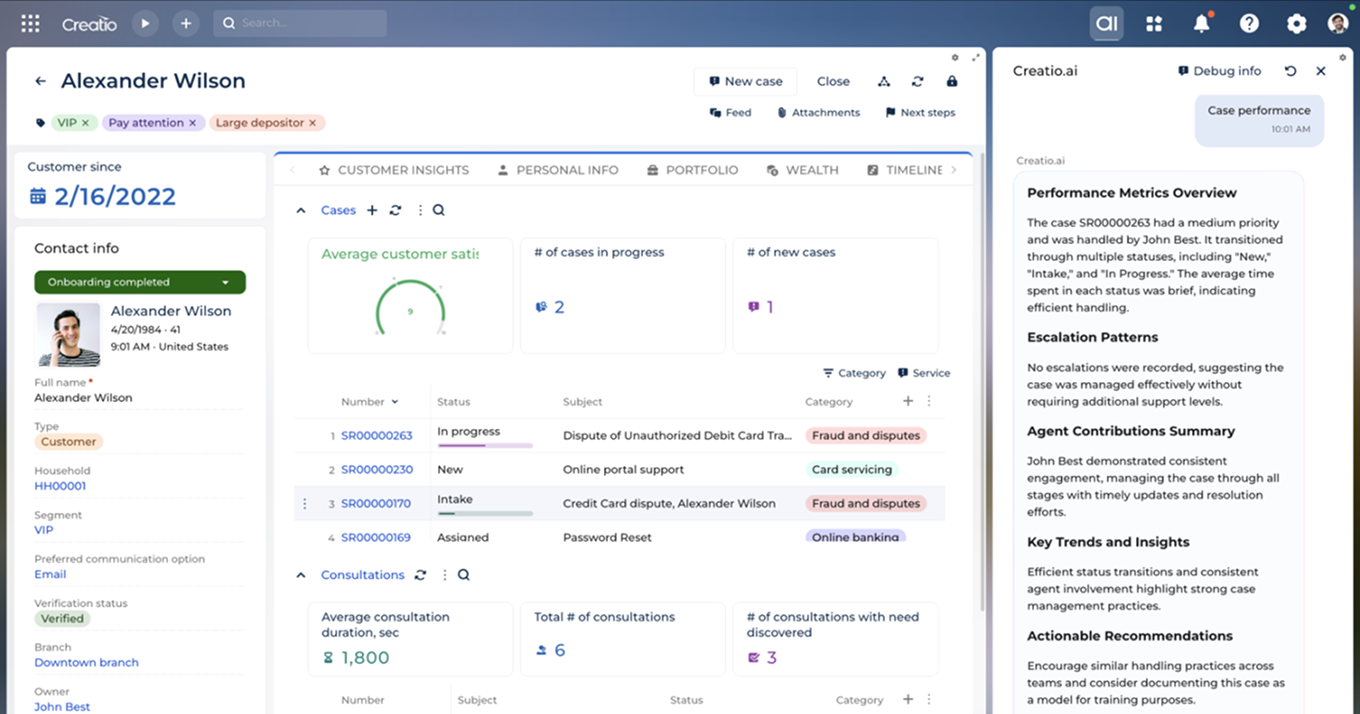
The platform also provides access to over 700 third-party applications, pre-built integrations, and connectors available through the Creatio Marketplace, allowing teams to tailor its capabilities to the specific requirements of any financial organisation.
With Creatio AI, finance teams are empowered to:
- Design and launch AI agents for specific financial workflows using powerful no-code tools without requiring deep technical expertise.
- Make real-time decisions relating to credit, risk, compliance, and operations through AI-native, context-aware agents.
- Continuously analyse both structured and unstructured data to uncover valuable insights and patterns as they emerge.
- Autonomously execute routine and complex tasks, such as updating records, generating reports, adjusting exposures, and more.
- Seamlessly integrate AI agents across other platforms to support efficient, scalable team workflows.
At Creatio, financial professionals collaborate with AI agents, combining human expertise with AI-driven decision-making and execution to achieve new levels of operational efficiency. With a flexible “human-in-the-loop” model, teams can determine the degree of autonomy granted to each AI agent, ensuring the right balance between automation and oversight across various processes and scenarios.
Creatio provides a library of prebuilt AI Skills that can be tailored to fit specific tasks, financial tools, and business objectives. Financial AI agents can actively monitor workflows, surface real-time insights, recommend next-best actions, and integrate directly with productivity platforms such as Outlook, Teams, Zoom, and calendars. Thanks to intuitive no-code tools, users can embed AI agents within existing processes or design entirely new autonomous workflows aligned with the strategic goals. With built-in generative, agentic, and predictive AI capabilities – and the freedom to create custom AI Agents for specific financial workflows Creatio empowers teams to act faster, operate more efficiently, and deliver measurable business outcomes.


