-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
Risk Management for Credit Unions - Key Risk Factors and Management Strategies
Updated on
May 08, 2025
7 min read
Build Proactive Risk Management Strategies With Creatio

Risk management is a crucial process for all financial institutions, and credit unions are no exception. As member-owned organizations, credit unions must aim to strike a balance between reaching financial goals and protecting their assets.
In this article, we explore the key categories of risk that credit unions face and provide practical strategies for managing them effectively.
What is Credit Union Risk Management?
Credit union risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, monitoring, addressing, and reporting risks that could affect a credit union’s financial stability. It’s a structured, organization-wide approach that helps credit unions anticipate potential threats and take proactive steps to reduce their impact.
A key part of the risk management process is establishing a clear risk appetite - the level and type of risk a credit union is willing to accept. Risk appetite should guide all strategic and operational decisions, ensuring alignment between risk exposure, the institution’s strategic goals, mission, values, and regulatory responsibilities.
Overall, the goal of credit union risk management is to protect the institution’s financial well-being, safeguard members’ assets, and support regulatory compliance, such as NCUA requirements in the U.S.
Types of Risks Faced by Credit Unions
Credit unions face multiple risks, both internal and external, that can have a significant impact on their operations and financial stability.
Here’s a list of the most impactful risks:
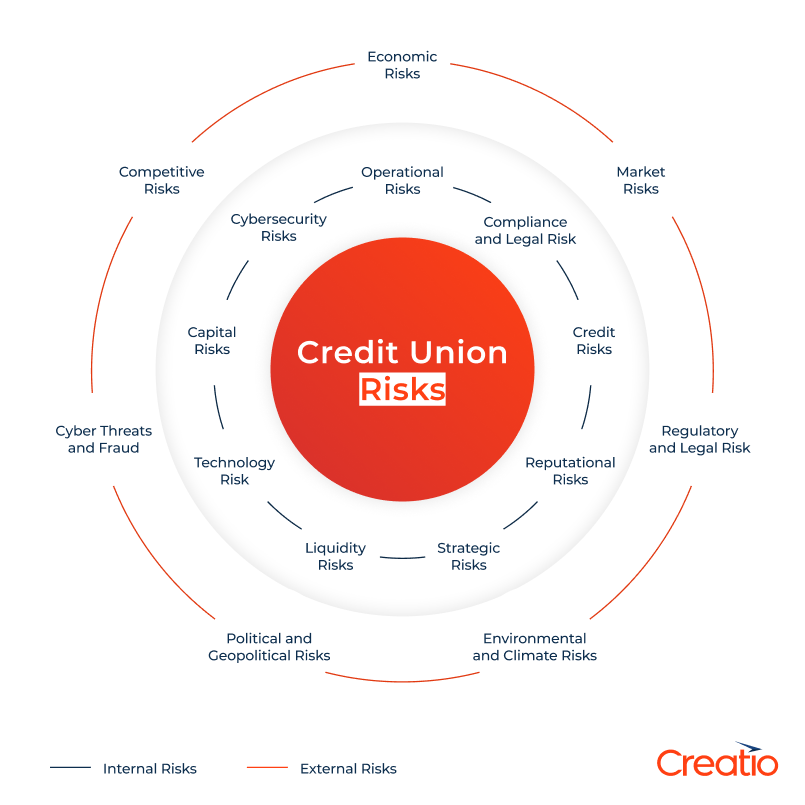
Internal risk factors
Credit unions have direct control, to a certain extent, over internal risks, such as operational practices, staff behavior, process efficiency, and internal systems.
Possible internal risk factors include:
- Operational risks - inefficient internal processes, system failures, or human errors can cause problems with operational efficiency. This can include bottlenecks, delays, and other issues.
- Credit risks - the possibility that borrowers may fail to repay loans on time or at all. This may be caused by inadequate loan underwriting or issues with accurate creditworthiness assessment.
- Strategic risks - negative impact of bad business decisions, poor strategic planning, improper implementation of decisions, or failure to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Reputational risks - damage to the credit union’s reputation and member trust can result from internal misconduct, poor service quality, or lack of transparency.
- Compliance and legal risk - violations of internal policies or legal requirements. This can be caused by inadequate staff training, failure to update procedures, or neglect to meet regulatory deadlines.
- Liquidity risks - inability to meet short-term financial obligations due to poor cash flow management or insufficient planning.
- Capital risks - insufficient capital reserves to absorb losses and support growth. This can be caused by poor planning, bad capital management, or unexpected expenses.
- Technology risk - outdated or unreliable IT systems can disrupt credit unions’ operations.
- Cybersecurity risks - system vulnerabilities that may lead to data breaches, unauthorized access, or loss of sensitive information due to a lack of robust security measures.
External risk factors
External risks on the other hand, cannot be controlled by credit unions since they arise from outside forces like economic shifts, regulatory changes, or cybersecurity threats. However, credit unions can still prepare to mitigate them through active monitoring and strong contingency planning.
Possible external risk factors include:
- Economic risks - external financial factors such as inflation, interest rate fluctuations, recession, or economic downturns that can affect members' behavior, borrowers’ ability to repay loans, and the credit union’s investment performance.
- Market risks - shifts in foreign exchange rates, stock prices, etc., can negatively impact credit institutions’ investment portfolios.
- Regulatory and legal risk - failure to adapt to changes in laws, regulations, or policies that credit unions must comply with can lead to fines, penalties, or operational disturbance.
- Competitive risks - pressure from other financial institutions, fintech companies, and digital banks. These competitors may offer more advanced digital services or better rates, making it difficult for traditional credit unions to retain or grow their member base.
- Environmental and climate risks - natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, or wildfires can damage physical assets, disrupt operations, or impact members.
- Cyber threats and fraud - unlike internal cybersecurity risk, this category focuses on external attacks such as phishing, ransomware, and fraudulent applications.
- Political and geopolitical risks - changes in government policy or legislation could impact credit unions. Geopolitical risk includes international events such as trade tensions, sanctions, or conflicts that may indirectly affect economic stability or investment decisions.
Strategies for Credit Union Risk Management
A robust risk management strategy allows credit unions to identify potential threats and address them proactively before they disrupt operations and damage financial health.
To facilitate creating a risk management strategy, we prepared a list of key strategies that credit unions can use to effectively manage risk across all areas of their organization:

1. Establish a risk governance framework
Credit unions should establish a well-defined governance structure that assigns roles and responsibilities in the risk management process. The board of directors and senior management should define the credit union’s risk tolerance and ensure policies and controls to support it.
2. Conduct regular risk assessments
Routine risk assessments help credit unions identify current and emerging risks across departments. This involves identifying and monitoring risks, evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each risk, prioritizing them, and determining appropriate responses.
3. Implement strong internal controls
To mitigate risks, credit unions should establish a robust set of internal controls. This includes clear policies, regular audits, approval workflows, and continuous staff training. Credit unions should also implement strong cybersecurity measures and appoint a dedicated risk management team to monitor risks in real-time and report to senior management.
4. Monitor Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Key Risk Indicators are metrics that signal changes in risk exposure and performance. By tracking KRIs, such as delinquency rates, liquidity ratios, or system downtime, credit unions can detect early warning signs and take actions to mitigate potential risks.
5. Ensure regular risk reporting
The risk management team should regularly provide risk reports to the board members, senior management, and regulators. Clear, consistent reporting helps drive informed decision-making, supports accountability, and promotes transparency across the organization.
6. Use technology to strengthen risk management
Modern risk management tools can automate data collection, enhance reporting accuracy, and support real-time monitoring. Credit unions can also use predictive analytics and risk modeling software to improve decision-making and stay ahead of threats.
7. Align risk management with strategic planning
Credit unions should consider risk management when developing short- and long-term strategies. This ensures that new initiatives, products, or partnerships are evaluated through a risk lens and that the organization is not unintentionally exposing its operations to additional threats.
8. Develop a disaster recovery plan
Credit unions should develop a disaster recovery plan to ensure they can continue operating during and after disruptions. This includes data backup protocols, communication plans, and alternative service channels for members. A comprehensive plan should also contain immediate actions to mitigate damage and a list of efforts for long-term recovery.
9. Leverage data insights
Predictive AI can support risk management by providing valuable insights. By analyzing external conditions and historical financial and operational data, AI can identify trends and potential risks that humans or simpler tools may miss during data analysis.
10. Provide ongoing risk management training
All credit union employees should understand the importance of risk awareness and know how to follow procedures designed to minimize risk. Regular training helps employees recognize potential threats, report issues early, and contribute to better risk management.
The State of AI Agents & No-Code: FinServ Edition
Learn how financial leaders use AI agents and no-code to fuel smarter transformation

Benefits of Having a Risk Management Plan for Credit Unions
An effective risk management plan is a strategic asset that can make a significant difference in operational resilience, financial performance, and long-term growth. Here are the key benefits of having a comprehensive risk management plan:
- Improved financial stability - by identifying potential financial risks, credit unions can take proactive actions to improve their financial stability, protect capital, and maintain adequate reserves.
- Stronger regulatory compliance - a structured risk management plan helps credit unions stay aligned with NCUA and state regulatory requirements, reducing the likelihood of penalties caused by non-compliance.
- Greater member trust and confidence - when members know their credit union is financially sound, secure, and responsive to emerging risks, it strengthens their trust.
- Better decision-making - risk assessments and reporting tools provide leaders with data-driven insights that support smarter strategic planning.
- Cost savings over time - preventing or minimizing losses through early detection and mitigation reduces financial and operational costs. In the long run, a strong risk management plan pays for itself by reducing costly incidents and improving resource allocation.
Credit Union Risk Management Software - Creatio Solution Tailored to Credit Unions’ Needs
As the risks that credit unions must face grow more complex, many credit unions are turning to specialized risk management software to enhance risk management. The most effective approach is to implement a CRM platform tailored to credit union needs that also supports robust risk management capabilities to protect the credit union's assets.
Tailored CRM doesn’t just manage member relationships, it becomes a centralized platform for compliance tracking, member risk profiling, and incident reporting.
A powerful solution in this space is Creatio, an AI-native no-code CRM and workflow automation platform with a robust set of tools tailored for credit union management. Creatio enables credit unions to configure risk management workflows, compliance tracking, and internal control processes without heavy IT support. Creatio's no-code environment enables credit unions to quickly adapt the platform to the evolving regulations and operational needs, improving risk resilience and service delivery.
With Creatio, credit unions can:
- Automate risk assessments and approvals
- Configure dashboards and real-time alerts
- Streamline compliance reporting and documentation
- Integrate with core banking and third-party systems
Creatio's unified approach to agentic, generative, and predictive AI allows credit unions to streamline crucial processes, including risk management, and derive deep insights that support decision-making.
Creatio Credit Unions CRM Implementation
Ent Credit Union transformed its operations with the Creatio no-code platform
With its powerful no-code tools and AI-driven capabilities, Creatio empowers credit unions to implement robust risk management processes and ensure the financial stability of their organizations.