-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
What is CRM Database & Why is It Important for Your Business
Updated on
July 14, 2025
10 min read
Turn CRM Data Into Actionable Insights. Try Creatio Now

Every customer interaction generates valuable data, and with the right systems in place, that data becomes a core business asset. A CRM database empowers organizations to structure, access, and activate this information, turning everyday interactions into strategic actions that drive engagement, efficiency, and growth.
In this guide, you will learn what a CRM database is, how it works, and the key types of data it manages. Additionally, you'll discover the benefits of CRM database software and how it can deliver measurable impact across your entire organization.
What is a CRM Database?
A CRM database is a core element of CRM (customer relationship management) software, designed to store, organize, and manage customer data within one platform. By providing a complete view of customer information — including contact details, communication history, purchase behavior, and preferences — a CRM database supports consistent and personalized experiences across all customer touchpoints.
CRM database software is commonly used across different departments, helping teams align and effectively manage customer interactions throughout the entire customer journey. For example, marketing teams use the CRM database to segment audiences, run targeted campaigns, and track lead engagement. Sales teams can use this data to identify high-potential leads, personalize outreach, and close deals more efficiently. Customer service teams rely on CRM database systems to quickly access client histories, resolve issues faster, and deliver a more personalized support experience.
When Businesses Turn to CRM Database Software?
Before companies adopt CRM database systems, they often struggle with recurring, costly challenges that affect customer satisfaction and business growth. The common issues include:
- Scattered or inaccessible customer data, making teams overly dependent on a few key knowledge holders.
- Siloed or incomplete customer information, often siloed across platforms and teams, with the critical data being easily lost, overlooked, or outdated.
- Poor lead prioritization, where the resources are spent on low-value leads while high-potential opportunities lack engagement or are missed.
- Inconsistent follow-up process, causing promising leads to go cold and customer loyalty to decline.
- Inefficient workflows, where significant time and resources are spent on repetitive manual work and constant coordination to keep teams aligned.
- Limited visibility into performance and customer journey, making it difficult to identify bottlenecks, improve processes, or align teams around the key goals.
CRM databases help businesses address these challenges by centralizing customer data and streamlining how it’s collected, organized, accessed, and used to drive smarter decisions and better collaboration.
Types of Data in a CRM Database
At the heart of every CRM platform lies its most valuable asset: data. Whether you're automating sales, running targeted marketing campaigns, or delivering outstanding customer service, it all depends on the right data in the right place.
CRM database may include the following data segments: operational, analytical, and collaborative. Comprehensive CRM systems typically bring all three together to power smarter decisions, tighter workflows, and stronger customer relationships.
Operational Data
Primarily used by operational CRMs, this category includes real-time customer data that supports day-to-day business processes. This data typically powers workflows related to sales automation, marketing activities, and customer service management.
An operational CRM database typically covers:
- Contact and account information
- Lead and opportunity data
- Communication history
- Tasks and calendar events
- Support tickets and SLAs
Analytical Data
Used by analytical CRM systems, this type of data is used to turn raw records into actionable business insights. It typically supports reporting, segmentation, forecasting, and performance analysis to guide strategic decisions. For example, analytical data helps uncover customer behavior patterns, understand their preferences and pain points to help teams optimize the customer journey and improve conversion rates.
An analytical CRM database may include:
- Lead scoring and pipeline metrics
- Sales performance reports
- Customer lifetime value (CLV)
- Churn probability
- Customer satisfaction trends
Collaborative Data
Essential for collaborative CRMs, this data enables different departments to share insights, align on client needs, and coordinate efforts across the organization. It plays a key role in maintaining a consistent customer experience.
A collaborative CRM database typically includes:
- Internal comments and tags
- Shared files and documents
- Assigned ownership and role visibility
- Notes on client preferences or escalations
- Inter-team workflows and activity feeds
Popular Use Cases of CRM Database Systems
Modern CRM platforms offer various capabilities based on customer data, but more doesn’t always mean better. Implementing too many features at once can increase costs and overwhelm teams with tools they may not fully use or need.
To build strong customer relationships and improve cross-functional collaboration, your CRM database should cover the following key use cases:
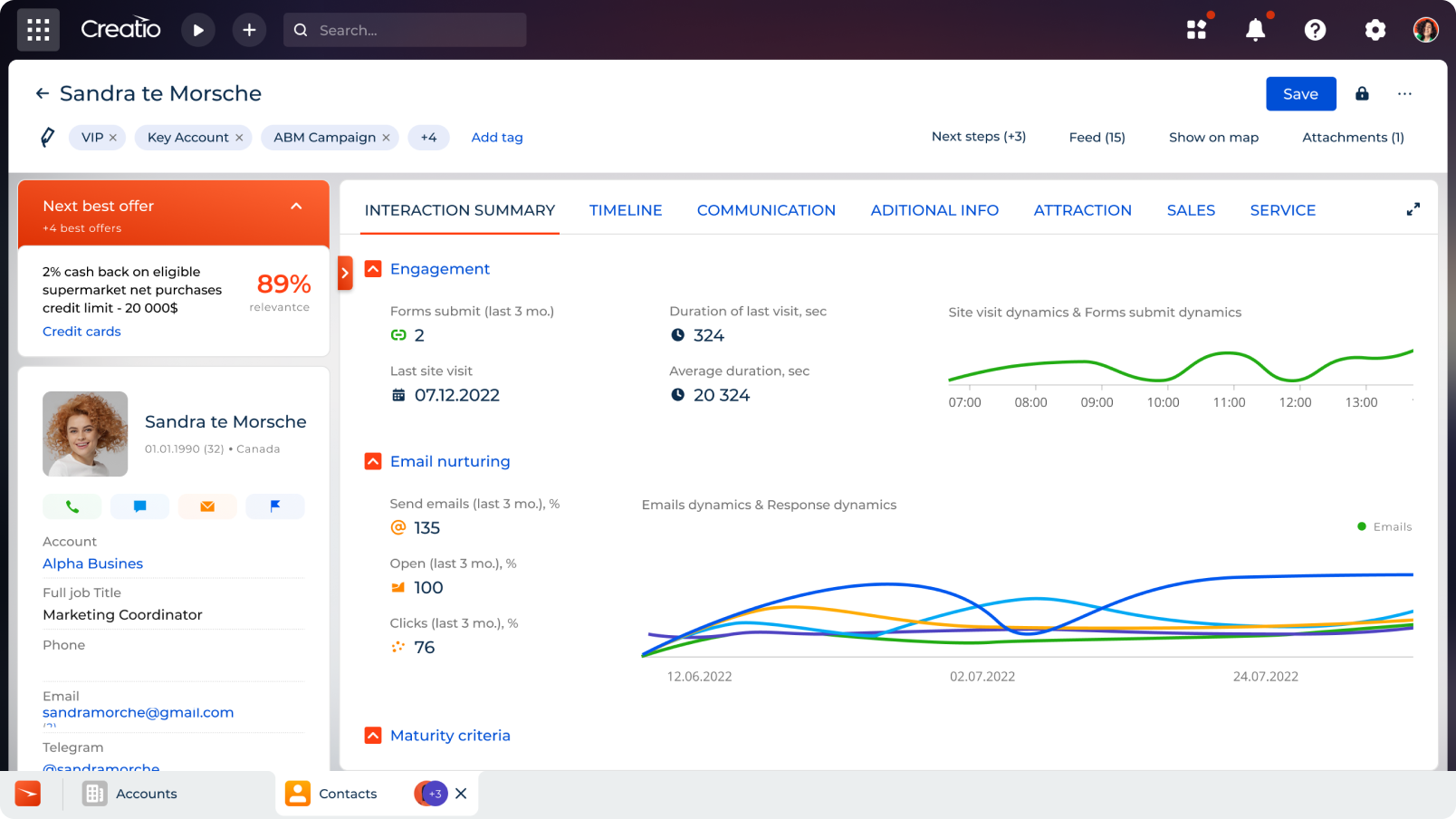
1. Contact & Accounts Management
At its core, a CRM database is designed to centralize customer data, helping teams easily identify clients and personalize interactions at any stage of their journey. It also ensures that all customer information is complete, accurate, and accessible, which is important for maintaining consistent communication across multiple channels and teams.
To effectively manage contacts and accounts, CRM database typically tracks:
- Customer contact information – Names, company details, phone numbers, email addresses, social media profiles, etc.
- Transaction data – Purchase history, order frequency, average spends, and most popular products
- Support requests – Tickets raised, resolution times, active and historical service records
- Communication logs – Calls, emails, follow-ups, pre/post-conversion engagement
- Important details and preferences – Preferred communication channels, specific requests, engagement level, and satisfaction scores.
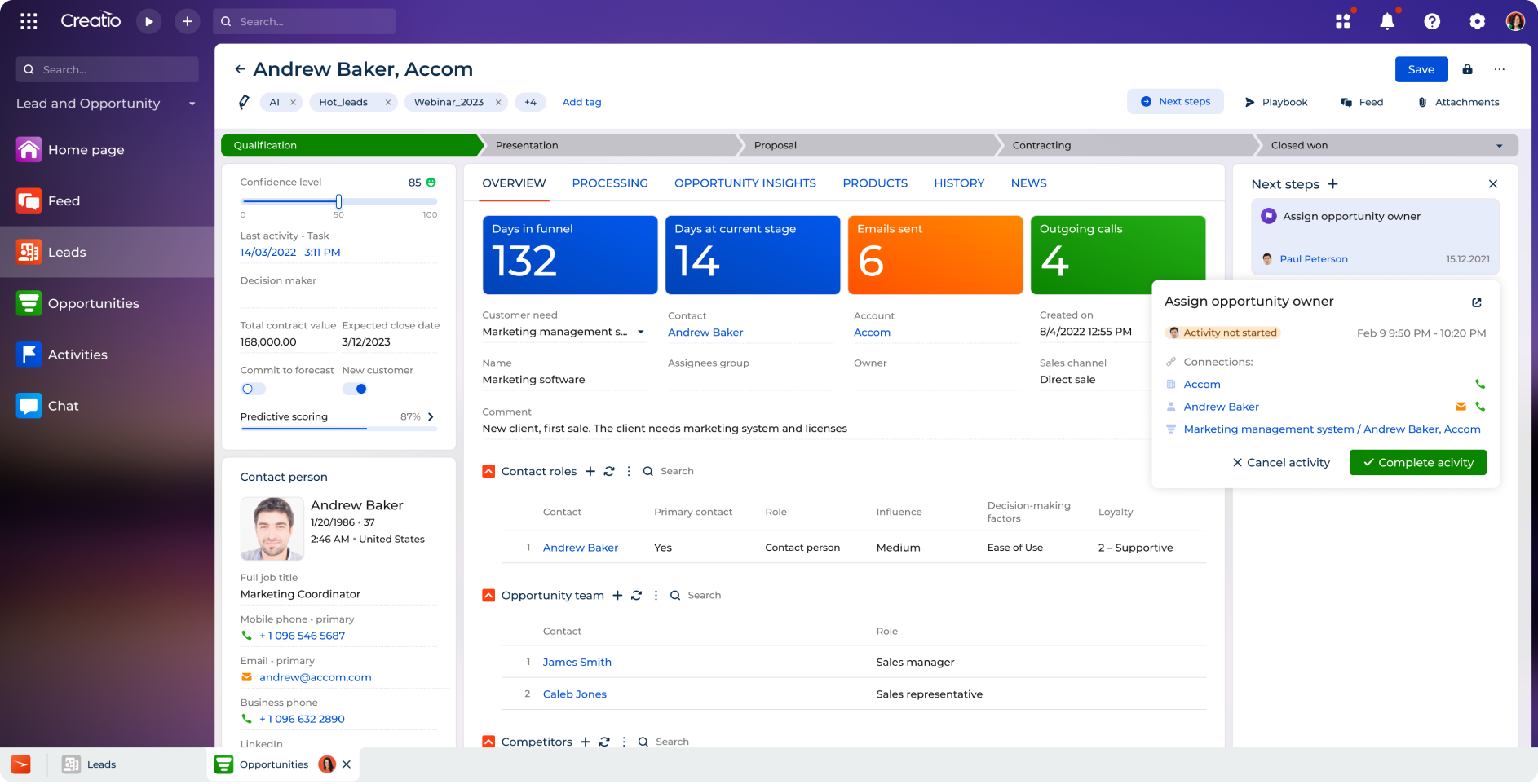
2. Lead Management
CRM database also plays the key role in capturing, managing and nurturing leads throughout marketing and sales funnels. In particular, it enables teams to align efforts on lead engagement, identify high-value prospects, and convert them more effectively based on the data related to:
- Lead source & Acquisition – Lead source, channel, and first touchpoint
- Pipeline & Qualification – Funnel stage, lead score, and qualification criteria
- Sales Activity – Communication history, associated customer service rep or account manager, deal value, and close date
- Customer behavior – Website activity, product interest, and event engagement
- Segmentation – Demographic and firmographic details
By analyzing the core lead data, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, prioritize the best sales opportunities, and approach prospects more effectively.
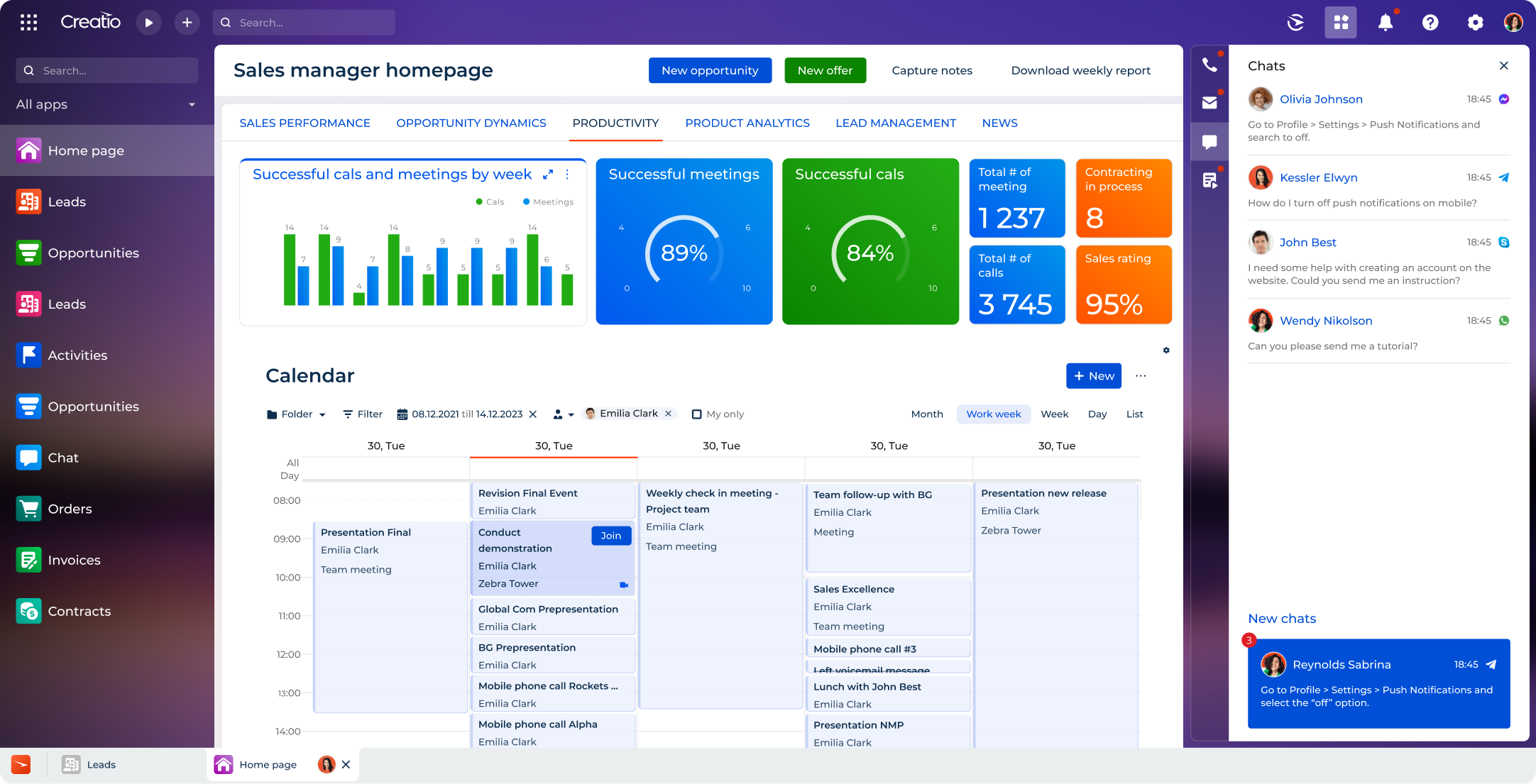
3. Team Collaboration
Smooth communication between teams is essential for delivering a consistent and efficient brand experience throughout the conversion funnel. According to Gartner, nearly 42% of businesses report that aligning marketing and sales teams is a key factor in accelerating the sales pipeline.
CRM databases support this alignment, working as a centralized hub with seamless access to up-to-date information. This approach enables businesses to keep their teams aligned, improve internal efficiency, and deliver consistent customer experience.
- Interaction history – Notes from calls, meetings, or emails
- Assigned tasks & Ownership – Task status, due dates and priority levels
- Internal comments and tags – Internal-only comments tied to contacts, deals, or tickets
- Document management & Shared files – Proposals, contracts, service agreements, onboarding materials,
- Individual and team performance data – Metrics that track activity, productivity, and outcomes
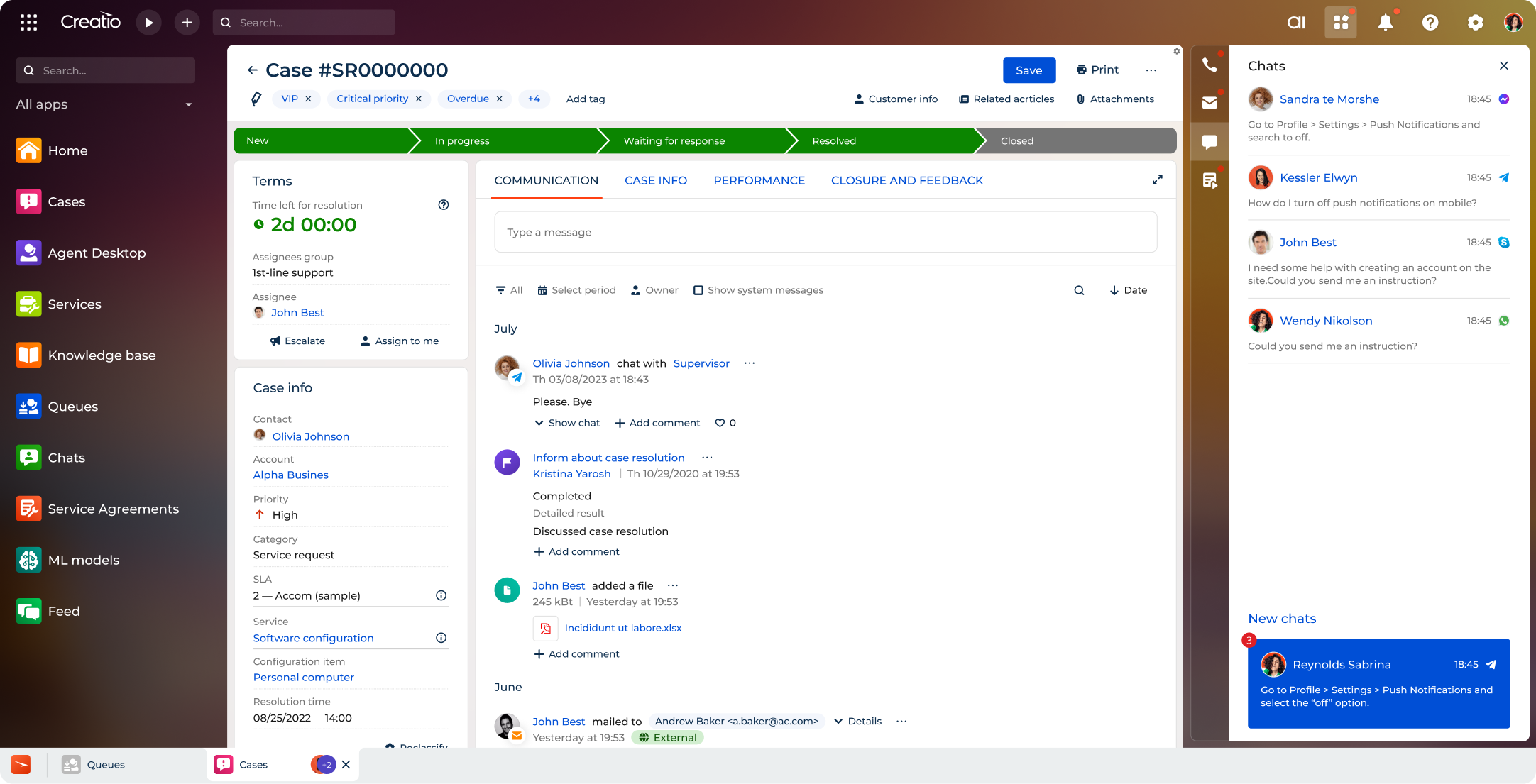
4. Customer Service
When prospects or clients have a question or run into an issue, whether before or after a sale, they expect its quick and effective resolution.
CRM database can enhance customer support by providing service teams with immediate access to relevant data, helping them effectively troubleshoot issues and share knowledge across departments. This includes access to:
- Logged support requests & Past interactions
- Issue descriptions and their resolutions
- Customer feedback & Satisfaction scores
- Support rep performance metrics
5. Data Analytics & Reporting
While more than 82% of enterprises use CRM solutions, almost every second of its users (48%) struggle to generate meaningful customer insights that support decision-making, according to Forrester. To avoid this gap, your CRM database should contain the right customer data to add context to performance metrics and uncover growth opportunities, particularly in marketing, sales, and customer service.
The most common analytics processes that can benefit from a CRM database are:
- Descriptive Analytics – Understand what has happened by analyzing past performance and user behavior
- Diagnostic Analytics – Determine why certain outcomes occurred by identifying patterns and underlying causes
- Predictive Analytics – Forecast future outcomes, such as churn risk or conversion likelihood, using historical and behavioral data
- Prescriptive Analytics – Recommend specific actions to improve results, such as when to engage a lead or how to optimize a sales strategy
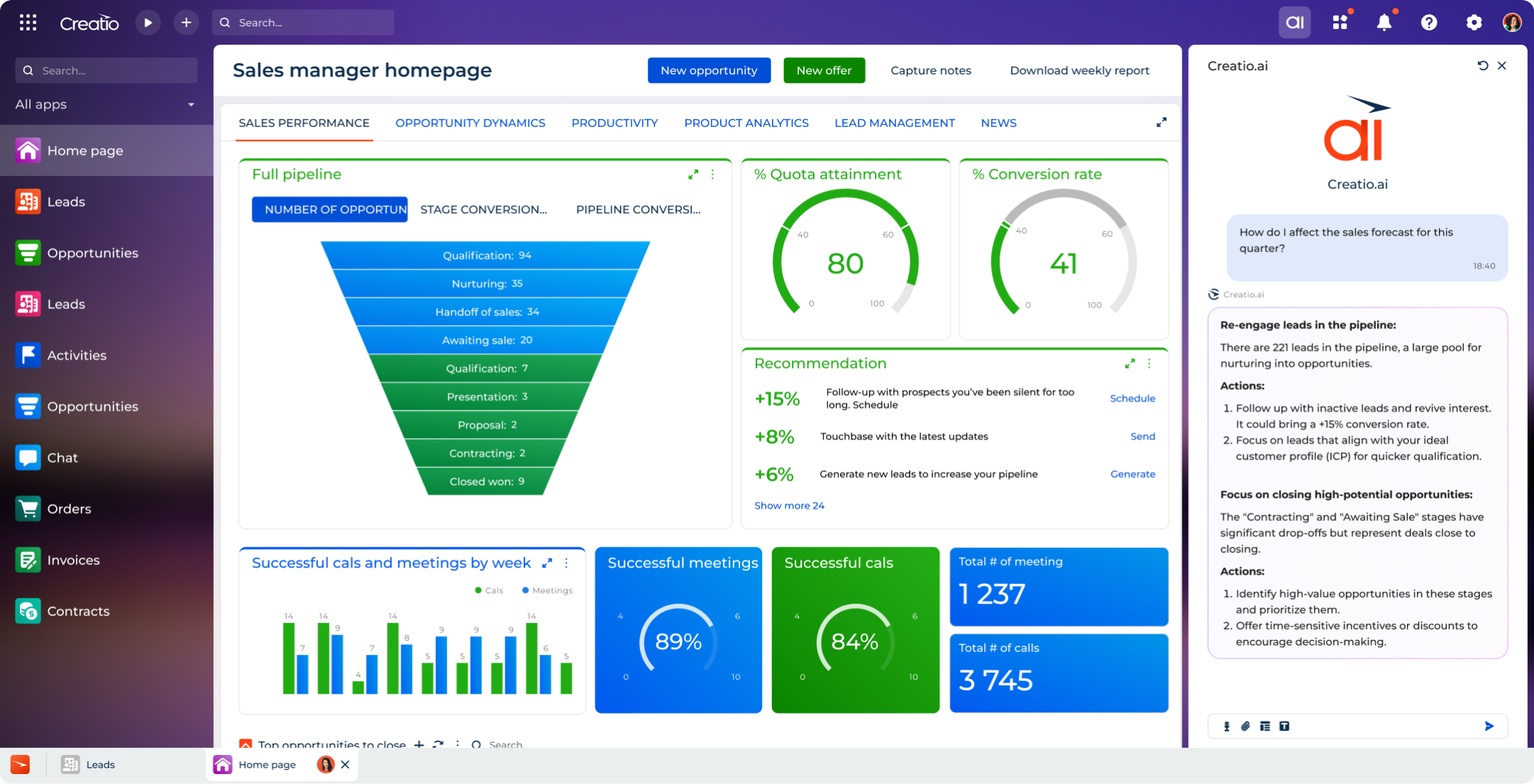
Key Benefits of CRM Database Software
A CRM database offers a wide range of benefits that help businesses maximize the value of their customer data. The most impactful advantages include:
Centralized Access to Customer Data
With a centralized approach to storing and organizing customer data, the CRM database ensures that every team across the organization is working with accurate, up-to-date information. A complete and consistent view of each customer allows businesses to enhance collaboration between departments, reduce data silos, and respond more quickly and effectively to customer expectations and needs. Unified access to CRM data also allows teams to gain insights about their clients, personalize engagement, and identify valuable opportunities to drive more sales and grow customer value.
Accelerated Sales Performance
By seamlessly collecting customer data, such as personal details, engagement, and purchase history, the CRM database enables teams to identify the right customers and prioritize high-value opportunities. Sales teams can effectively segment and score leads to focus their efforts on those most likely to convert. Additionally, CRM data helps sales professionals deeper understand customer preferences and needs, enabling them to uncover cross-sell and upsell opportunities throughout the customer journey.
Personalized Customer Experience
Companies that effectively manage and personalize the customer experience can achieve a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and a 15% boost in sales conversions, according to McKinsey. A CRM database can support these efforts by offering a complete view of customer data and behavior. With deeper insights into engagement patterns and preferences, businesses can determine the best time, channel, and message for each interaction with new leads and existing customers. As a result, CRM database enables teams to deliver more meaningful experiences, improving customer retention, and build stronger long-term loyalty.
Faster, Data-Driven Decision-Making
CRM databases offer a real-time, end-to-end view of the customer lifecycle by centralizing customer records, interaction history, and performance data. This visibility empowers teams to act on insights backed by actual customer behavior and performance trends. For example, sales teams can spot trends in customer preferences and adjust their sales strategies on the fly. Marketing teams use CRM database insights to identify triggers that drive engagement for specific audiences. Service teams can pinpoint recurring issues and build proactive strategies to improve customer support interactions.
Types of CRM Software for Database Integration
The deployment model of a CRM system — on-premise or cloud-based — directly impacts how its database is stored, integrated, and maintained. Each option offers different levels of control, accessibility, and responsibility for managing CRM data.
The table below highlights key differences in CRM database management for each model.
On-premise CRM software | Cloud CRM solutions | |
| Deployment Method | CRM systems are installed and run on a company’s own servers and infrastructure. | Ready-to-use CRM software that is hosted and managed by an external provider. |
| Database Management | These systems offer full control over the CRM database and underlying infrastructure. | The system’s database is hosted and maintained by the CRM vendor in the cloud. |
| Best for | Organizations with strict data security or compliance requirements, where full control over data is critical.
| Businesses that prioritize fast deployment, lower upfront costs, automated updates and maintenance. Ideal for teams with limited internal IT resources. |
While both CRM deployment models have their advantages, many enterprises are moving toward cloud-based systems for flexibility, lower upfront costs, and scalable infrastructure. According to Grand View Research, cloud CRM software dominated the market in 2024, accounting for 58.2% of total industry revenue.
Gain More Insights from Client Data with Creatio CRM
Choosing the right CRM platform is essential for getting full control over your customer data, from how it’s captured and stored to how it’s analyzed and used. A well-structured CRM software acts as a centralized database across the entire organization, empowering teams to turn data into actionable insights, improve decision-making, and deliver personalized experiences to new and existing company’s customers.
Creatio CRM is a comprehensive CRM suite of products for marketing, sales, and service automation integrated on a unified no-code platform and enhanced by modern AI capabilities. It enables businesses to centralize and manage customer and account data, streamline lead and opportunity management, deliver personalized customer interactions and automate the full customer lifecycle — all from a single, flexible CRM system.
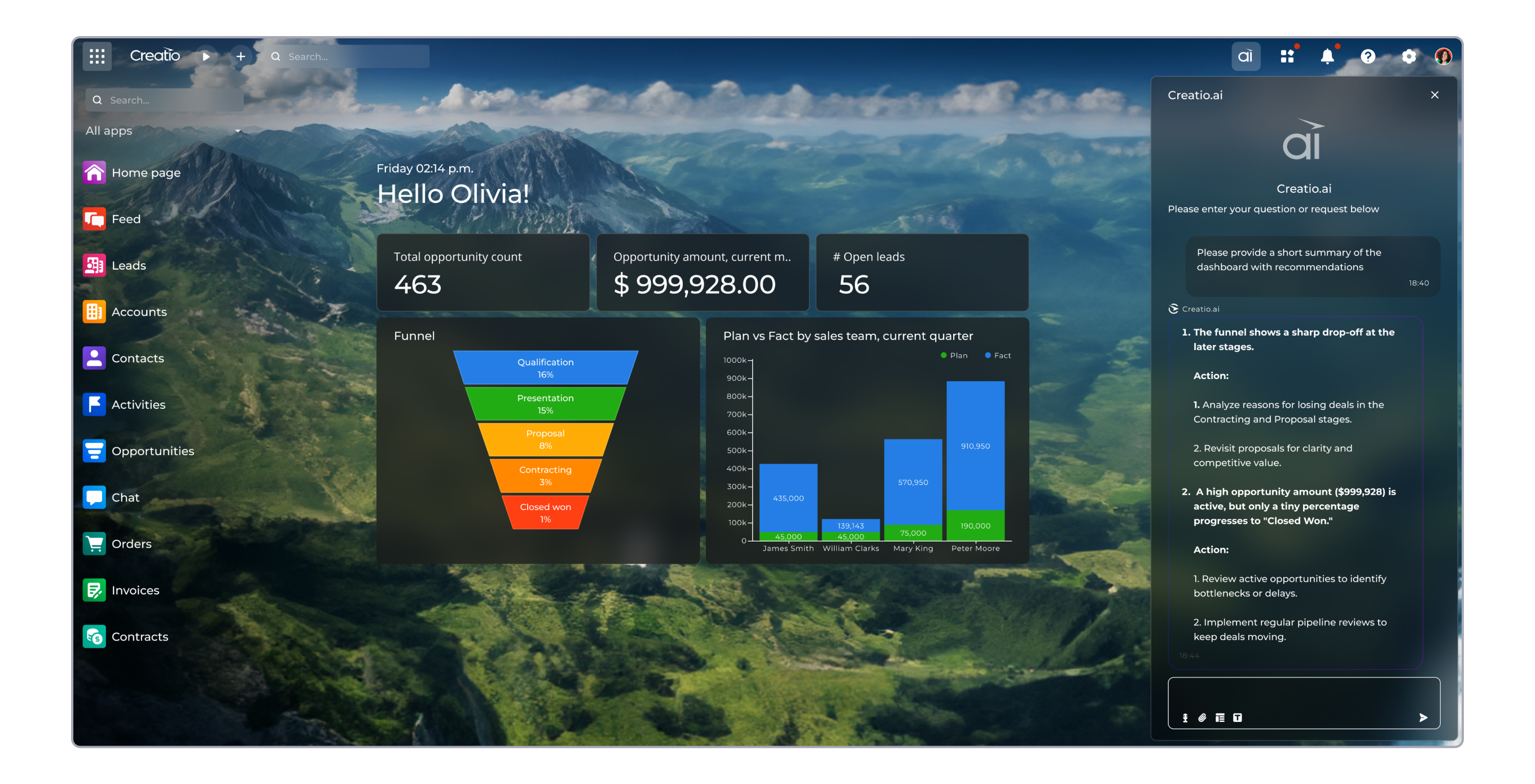
Creatio products can be deployed as an all-in-one CRM bundle or as standalone solutions to match exact goals and needs of your business. Its composable solution for customer relationship management includes:
- Creatio Marketing - a ready-to-use platform to automate marketing campaigns and lead management workflows with no code and a maximum degree of freedom. It is a popular solution that helps businesses gain a holistic view of customer data, run omnichannel marketing campaigns, orchestrate customer journeys, streamline digital campaigns, email and event marketing, and enhance team collaboration.
- Creatio Sales - an end-to-end platform to automate sales processes of any type with no-code and a maximum degree of freedom. This product provides a 360-view of contacts and accounts, helps companies automate lead and sales processes, run forecasts, streamline order and document management and ensure efficient collaboration between members and teams.
- Creatio Service - an omnichannel platform to automate customer service workflows of any complexity with no-code and a maximum degree of freedom. This product allows businesses to build a holistic customer view for smarter service delivery, organize traditional and digital helpdesk operations, enhance employee productivity and foster team collaboration, and implement enterprise-grade automated service workflows powered by no-code customization and agentic AI capabilities.
Creatio CRM integrates key AI patterns – generative AI, agentic AI, and predictive AI, helping businesses to unlock new levels of efficiency, personalization, and data intelligence. Predictive AI can analyze historical customer data to forecast behavior, identify high-value leads, and recommend next-best actions to help teams enhance customer interactions and meet their expectations. With Generative AI, teams can automate content creation, personalize messages, and campaign materials based on customer profiles. Meanwhile, agentic AI takes automation further by acting as a virtual assistant that autonomously performs tasks like updating records, scheduling follow-ups, or orchestrating complex workflows — all while continuously learning from CRM data.
Additionally, Creatio CRM provides a composable no-code architecture that allows businesses to customize their solution to their unique needs, without requiring IT assistance. Thanks to integration with over 700 third-party tools and applications, teams can easily implement tools from their existing tech stack into one cohesive CRM system. This connectivity ensures a seamless flow of operational and customer data across the entire business ecosystem.
With millions of industry-specific workflows launched daily across over 100 countries, Creatio empowers organizations to streamline operations, orchestrate complex customer journeys, and turn large volumes of data into real business value.
Drive business growth with one composable CRM solution






















































