-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
What are AI Agents? How AI Augments Human Work to Increase Productivity
Updated on
March 04, 2026
20 min read
Accelerate Lead Response Time by 61% With Creatio

Have you ever dreamt of an extra pair of hands to tackle your piling workload? With AI agents stepping in, that dream is now a reality. They're here to automate repetitive tasks, solve complex problems, and help you make smarter, data-driven decisions. With the AI agent market expected to grow from $7.84 billion in 2025 to $52.62 billion by 2030, and 86% of C-level decision-makers believing AI agents will be strategically important over the next two to three years, their presence in our daily work is only going to expand.
In this article, we will cover what an AI agent is, how it works, and how it can enhance human skills, increasing productivity and efficiency.
Key Takeaways:
- AI agents are intelligent software systems that can perceive their environment, reason, plan, use tools, and perform tasks to achieve specific goals with minimal human supervision.
- The basis of AI agents is an agentic architecture that combines foundation models, memory, planning modules, and tool integrations to analyze context and execute multi-step tasks.
- Agents work through a continuous sense-plan-act-reflect cycle, which enables them to learn from past interactions and improve their performance over time.
- The benefits of AI agents include enhanced productivity, increased accuracy and consistency, improved customer satisfaction, high scalability, cost effectiveness, and data-driven decision-making.
- Agentic platforms like Creatio enable organizations to deploy, orchestrate, and manage AI agents at scale, combining CRM, workflow automation, and no-code tools to accelerate intelligent automation across business processes.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents (artificial intelligence agents) are software systems that can act autonomously with minimal human intervention by perceiving their environment, reasoning, planning, using tools, and taking actions to achieve goals on behalf of users.
They use technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and large language models (LLMs) to analyze data, make decisions, and perform actions that complete assigned tasks. Unlike assistants or chatbots that follow pre-defined rules or only generate text, AI agents can execute complex, multi-step tasks. What’s important to note is that AI agents are designed to augment human capabilities and optimize efficiency by working alongside humans, rather than replacing them.
Autonomous AI agents operate using agentic AI technology, which enables them to act independently by sensing inputs, reasoning, calling on external tools, and making decisions on the best response to achieve goals set by human users. Advanced agents can also learn from the outcomes of past actions to improve their performance and continuously adapt to changing conditions and user expectations.
Intelligent agents support users in their daily work by automating repetitive tasks, surfacing valuable insights, solving complex problems, and facilitating seamless interactions with users or other systems.
The State of AI Agents & No-Code
Learn how 560+ leaders across the world use AI and no-code to drive innovation today
Key Components of AI Agent Architecture
Behind agent technology is a structured architecture that enables it to perceive inputs, reason about what needs to be done, act on that reasoning, and improve over time. AI agents rely on a coordinated system of components that work together to deliver autonomous functionality:
- Foundation model is a large language model (LLM) that lies at the core of an agent and serves as its reasoning engine, or “the brain”. It powers the agent's ability to interpret natural language, analyze context, perform a multi-step reasoning process, and generate responses.
- Memory module equips agents with short- and long-term memory, enabling them to retain context, learn from past experiences, and refine their performance. Short-term memory stores information about current interactions and chat history, and long-term memory stores historical data and previous conversations. To retrieve relevant knowledge, documents, and data, agents use vector databases or knowledge graphs.
- Planning module allows agents to break down complex, large-scale goals into smaller, more manageable tasks and consider multiple dependencies to decide on the best approach to achieve the objectives.
- Tool integration connects the agent to enterprise systems, APIs, and external software, allowing it to interact with its environment and perform tasks such as retrieving third-party data, updating records, triggering workflows, sending communications, and controlling hardware.
- Governance & guardrails ensure responsible and secure operation through human-in-the-loop oversight, policy-based AI controls, and audit trails.
How Do AI Agents Work?
Artificial intelligence agents operate through a continuous sense-plan-act-reflect cycle, mimicking how we humans process information and take actions. This allows them to understand their environment, make informed decisions, and execute tasks autonomously.
The process can be broken down into 4 key stages:
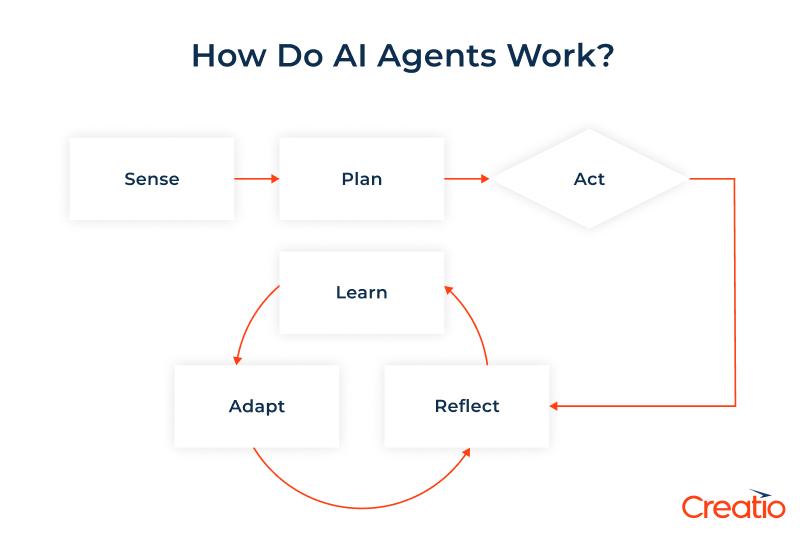
Sense
In the first step, the AI agent perceives and understands information from various sources. It leverages tools, such as APIs, databases, web scraping, or direct data feeds, to search through internal databases and external sources. An AI agent can process text, images, and data and comprehend natural language requests. Additionally, it can collaborate with other agents to exchange information, ensuring it has the comprehensive view needed to complete its goals.
Plan
Once it gathers the required information, the agent uses its algorithms, internal models, and knowledge bases to formulate a plan. This is where technologies like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and large language models (LLMs) come into play:
- ML algorithms enable the agent to identify patterns, make predictions, and learn from data.
- NLP allows AI agents to understand natural language, which is crucial for interacting with users, understanding instructions, or interpreting textual information.
- LLMs provide advanced contextual understanding, complex problem-solving capabilities, and the ability to generate human-like responses.
Using these algorithms, the AI agent analyzes gathered data, understands user-defined goals, and maps potential solutions. AI breaks down complex problems into manageable steps, determines the necessary actions and their sequence, and plans how to handle potential obstacles. This process often involves complex planning, problem-solving, and risk assessment.
Act
Next, the AI agent puts the plan into action, executing tasks in a correct sequence. These actions vary depending on the goal and context. For example, the agent might send notifications or emails, update or retrieve records from databases, or perform real-time data analysis to support decision-making. In more complex scenarios, the agent may perform multiple steps simultaneously or work within multi-agent systems to complete tasks.
Reflect
A hallmark of advanced AI agents is their ability to reflect, learn and adapt. After the agent performs a task, it evaluates the results and gathers users’ feedback to understand whether its actions were successful, and if not, what went wrong.
To improve future performance, the AI agent updates its internal models and knowledge base, supporting effective strategies while changing those that proved less successful. This feedback loop, often driven by techniques like reinforcement learning, allows the agent to make better decisions and, over time, become more accurate and effective in achieving its goals.
While intelligent agents are designed to operate autonomously, human oversight remains essential to ensure that these agents behave as intended. The human in the loop (HITL) approach involves human oversight at various stages, allowing users to monitor, review, and adjust an agent's decisions or actions.
Human intervention is important to improve agents’ performance, address potential biases, and maintain alignment with organizational goals. HITL is especially important in industries where AI outcomes can have significant real-world consequences, such as healthcare and financial services. The human-in-the-loop collaborative model underscores that AI agents are powerful tools designed to extend human capabilities but cannot replace the need for human judgment and emotional intelligence.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be classified in several ways - based on decision logic, memory, autonomy level, and collaboration structure. These foundational differences shape how agents behave and determine the kinds of tasks they can support within business environments.
Below are the most common types of AI agents, listed from the simplest to the most advanced:
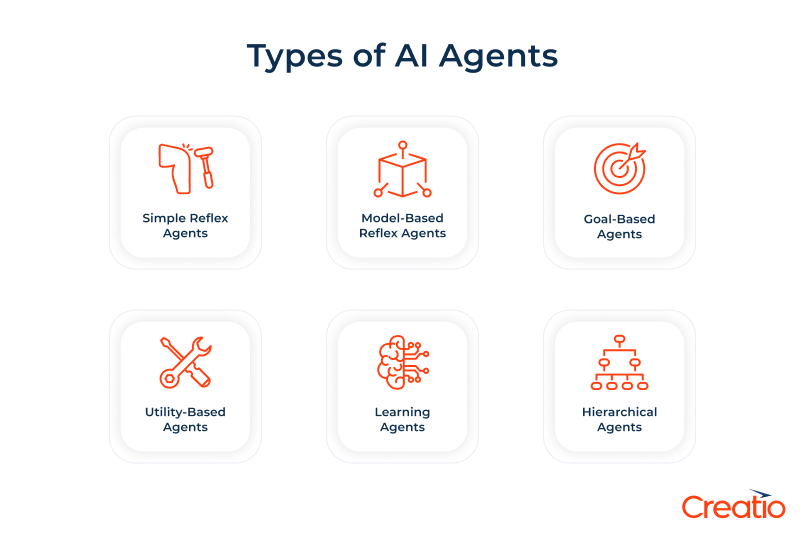
1. Simple reflex agents
- How they work - these are the most basic types of AI agents designed to perform simple, well-defined tasks. They work using a set of predefined rules, executing pre-programmed actions whenever a specific condition is met. They consider only the current state of the environment; they don’t have any memory of past experiences and do not consider future consequences. As a result, they are unable to evaluate their performance or adapt to unexpected situations that go beyond predefined scenarios and rules.
- How they support humans - simple reflex agents are best suited for automating highly repetitive, routine tasks in predictable environments. They free up humans from administrative work and simple decisions.
- Example - as soon as a new contact is added to a marketing list, an AI agent sends a "Welcome" email.
2. Model-based reflex agents
- How they work - unlike simple reflex agents, model-based agents use their current perception as well as memory to build an internal model of the environment to support their decisions. This model represents the world's current state and how it evolves over time, allowing the agent to consider past experiences and probable outcomes when making decisions. The AI model is also updated once new information is available.
- How they support humans - model-based reflex agents can assist humans with more complex tasks, as they can adapt to dynamic environments to make the right decision.
- Example - AI agent tracks stock levels, predicts future needs, and automatically orders new supplies.
3. Goal-based agents
- How they work - these agents are designed to achieve specific outcomes. Unlike reflex agents that react to inputs, goal-based agents evaluate different options and choose the best path to reach a defined goal.
- How they support humans - goal-based agents are helpful when the end result is known. They don’t need detailed instructions or pre-defined rules to complete a task.
- Example - an AI agent manages the invoice process by checking that all required data and signoffs are in place before marking it as approved.
4. Utility-based agents
- How they work - the most sophisticated type of rational agent, utility-based agents go beyond simply achieving a goal. They evaluate potential actions not just by whether they achieve a goal, but by how well they achieve it, considering factors like efficiency, cost, risk, etc. They choose the action that can bring the best results.
- How they support humans - utility-based agents assist in complex decision-making processes, considering multiple factors, and recommending actions to maximize the desired outcome.
- Example - AI agent intelligently routes incoming support tickets to agents based on the customer's complaint, the agent's experience, current queue lengths, and the urgency of the issue, optimizing both customer satisfaction and agent workload.
5. Learning agents
- How they work - Learning agents improve over time by analyzing past experiences and external feedback. They typically include a learning element that updates their behavior, a critic that evaluates performance, and a problem generator that suggests new actions to try.
- How they support humans - learning agents adapt to changing conditions and user behavior without needing to be reprogrammed. They help optimize business processes by continuously improving how tasks are performed, reducing the need for manual adjustments.
- Example -This AI agent continuously learns which specific lead actions (website pages visited, email open rate, etc.) are the most important predictors of successful conversions and automatically adjusts its lead scoring model.
6. Hierarchical agents
- How they work - these sophisticated AI agents are built in layers. A high-level agent interprets the user’s goal, breaks it into smaller tasks, and assigns those tasks to lower-level agents that carry them out.
- How they support humans - hierarchical agents automate complex tasks and orchestrate large-scale business processes that involve multiple steps.
- Example - A group of AI agents manages the entire customer lifecycle. The top-level agent oversees the full journey, while other AI agents handle acquisition, onboarding, retention, and re-engagement.
7. Multi-agent systems
- How they work - multiple AI agents form agentic AI systems to complete tasks and achieve shared goals. Each agent has a specialized role and can communicate, coordinate, exchange data, and dynamically delegate tasks to others. An orchestrator agent oversees the process, directing specialist agents and aligning their activities to tackle complex tasks.
- How they support humans - multi-agent systems enable organizations to automate and manage complex, cross-functional processes. By distributing tasks across other agents, they improve efficiency and adaptability, especially in environments where complex workflows span multiple departments or systems.
- Example - a network of AI agents can support customer service operations. One agent handles customer requests, another retrieves relevant knowledge base content, and a third updates CRM records.
Benefits of AI Agents
The integration of AI agents into business operations can bring multiple benefits, from increased productivity to smarter decision-making.
These are the most important benefits of AI agents:
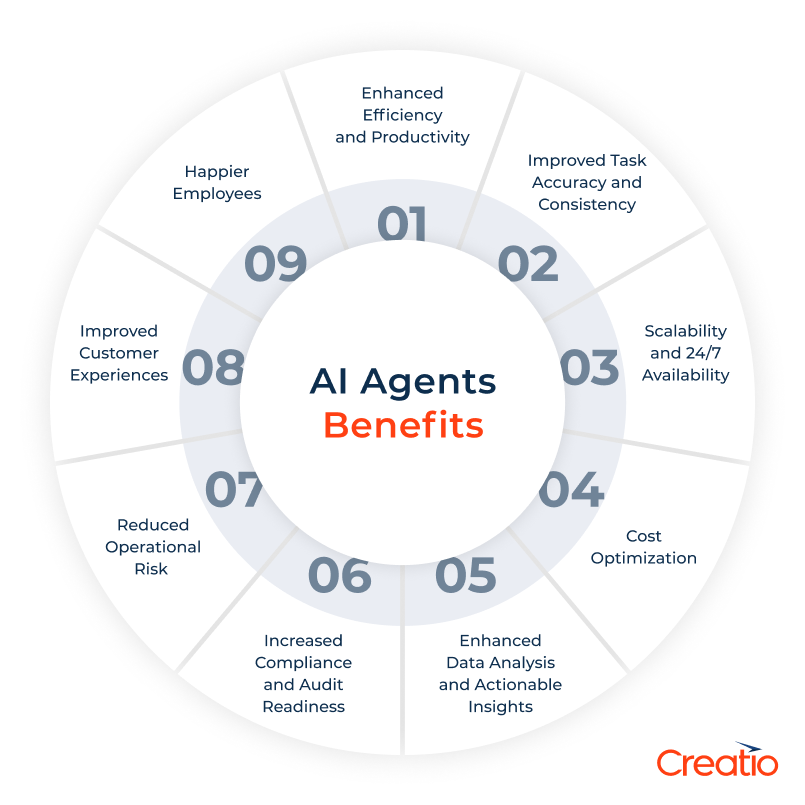
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity - AI agents can automate repetitive and mundane tasks that traditionally consume a lot of employees' time. Tasks such as data entry, routine inquiries, lead assignments, or standard report generation can be handled by AI agents, freeing humans to focus on more complex, strategic, and creative work that requires uniquely human skills.
- Improved task accuracy and consistency - AI agents are designed to follow instructions precisely and apply rules consistently. They help reduce manual errors in data entry, transaction processing, and routine decision-making. While not infallible, AI agents improve the overall accuracy and reliability across repetitive tasks.
- Scalability and 24/7 availability - unlike humans, AI agents don't need to take breaks to sleep or eat and can operate around the clock. This allows businesses to scale their operations to handle increased demand without employing additional staff. With autonomous agents, businesses can provide uninterrupted, high-quality service and support, even outside business hours. According to Gartner, by 2028 AI agents will handle 20% of interactions across the buyer's journey.
- Cost optimization - by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing errors, AI agents enable significant cost savings. This includes reducing labor costs, minimizing expensive errors, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced data analysis and actionable insights - intelligent agents can process and analyze vast amounts of data much faster than traditional systems, let alone human analysts. This capability allows them to identify patterns and trends, and surface actionable insights, empowering businesses to make informed decisions regarding planning, forecasting, and problem-solving.
- Increased compliance and audit readiness - by following predefined workflows and rules with precision, AI agents help ensure that regulatory processes are executed consistently. They also generate clear logs and audit trails, making it easier for organizations to demonstrate compliance.
- Reduced operational risk - through standardization, automation, and continuous monitoring, AI agents help reduce the risk of human error, process deviations, and delays, especially in mission-critical operations such as payments, approvals, or onboarding.
- Improved customer experiences -AI agents can support customer service professionals by providing instant responses to common queries and route complex issues to the right human agent with full context. This enables customer support teams to resolve issues faster, personalize interactions, and improve customer experience.
- Happier employees - by taking over the tedious and time-consuming aspects of their roles, AI agents allow human employees to spend more time on high-value activities such as building relationships, innovating, and developing new strategies, leading to higher job satisfaction.
Real-Life Examples of AI Agents Use Cases
AI agents already operate in many aspects of our digital world, often working behind the scenes to enhance efficiency, improve user experience, and support smarter decision-making. According to Creatio’s The State of AI agents & No-Code report, over 40% of AI agents are being deployed in frontline-growth functions, including sales (14 %), marketing (13 %), service (12 %), and customer success (7 %). This trend showcases the growing role of deploying AI agents in driving transformation and shaping competitive advantage.
Let’s explore several real-world applications that demonstrate how you can leverage AI agents in your business:
Intelligent lead scoring and routing
An AI agent monitors incoming leads from all channels, including the website, social media, and digital events, such as webinars, product releases, etc. It analyzes prospects’ data (company size, industry, behavior on your site, past interactions) against predefined ideal customer profiles and assigns a qualification score. Based on this score, the agent automatically routes high-potential leads to the most appropriate sales rep, provides summary of crucial information, and suggests next-best-action to win a deal faster.
Find out more about how AI sales agents augment sales representatives’ work
Customer support automation
AI agents can be deployed in the form of intelligent chatbots or virtual assistants to take care of incoming customer queries. These agents can answer frequently asked questions, resolve basic issues, and perform simple tasks on behalf of clients, such as checking their order status or filling out a return form. By involving AI agents in the customer support processes, businesses can improve response times and overall customer satisfaction.
Marketing campaign automation and optimization
AI agents in marketing platforms can automatically segment audiences, personalize content to customer needs, and trigger multi-step email campaigns based on user behavior. For example, an autonomous agent can send a series of follow-up emails after a webinar registration or adjust the ad budget based on campaign performance.
Additionally, an AI agent can help maximize conversion rates by analyzing performance metrics, such as open rates, click-through rates, etc., in real time. To improve campaign outcomes, an agent autonomously adjusts specific elements, such as email headings or ad visuals and performs A/B tests to find the most effective version.
Gartner predicts that by 2028, 60% of brands will use AI agents to deliver hyper-personalized, autonomous experiences.
Intelligent meeting scheduling
AI agents can schedule meetings with clients, coordinating multiple calendars, preferences, and time zones. They can find optimal time slots across all participants, automatically send invites, update calendars, and reschedule if the meeting needs to be postponed. Additionally, AI agents can update CRM (customer management system) records with meeting details and outcomes, providing a valuable summary.
Dynamic product recommendation
E-commerce businesses can use autonomous AI agents to automatically generate and display personalized product recommendations based on individual customers’ shopping carts, website behavior, online activity, etc. Moreover, AI agents continuously gather new data and update their recommendations in real time to reflect current customer needs and preferences.
Sales representatives can also use insights surfaced by AI agents to personalize sales offers to each client and provide tailored cross-/upselling recommendations to increase deal value.
Knowledge retrieval
If a sales representative or a customer service agent needs to quickly access specific product information, customer account, policy details, etc., during a call or a meeting, an AI agent can find and surface this information for them. Integrated with the company’s CRM and knowledge base, AI agents can instantly access required information, create a summary, and even suggest the best response, acting as a real-time assistant.
Industry-specific AI agents
According to Markets and Markets research, the market for industry-specific AI agents is expected to grow by over 35% in the next 5 years. This includes agents designed for specific functions in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and legal sectors, often integrated deeply into industry-specific software and workflows.
Here are a few examples of tasks that industry-specific agents can perform:
- Healthcare - AI agents assist healthcare workers by automatically scheduling patient visits, updating medical records, and processing insurance claims.
- Finance - financial institutions can use finance AI agents to automate fraud detection, credit scoring, and regulatory compliance checks.
- Manufacturing - AI agents can monitor equipment performance, manage inventory, and optimize supply chains.
Challenges of Using AI Agents
While AI agents have enormous potential for transforming business operations, their implementation and ongoing management can be challenging.
When asked about barriers to broader adoption of AI agents, over 50% of business and technology decision-makers cite data quality and system integration, 43% regulatory, security, or legal concerns, and 26% cite change management.
The most common challenges of using AI agents include:
Challenge | Solution |
| Access to high-quality data | Implement robust data governance frameworks, use automated data validation and cleansing tools. |
| Complex implementation & integration | Choose a vendor (e.g., Creatio) that natively integrates AI agents into their system to accelerate time to value. |
| Ethical concerns and bias | Implement strong governance policies and responsible AI practices in development and review. |
| Lack of transparency | Select AI agents that provide maximum transparency in their decision-making processes. |
| Security and privacy risks | Find a vendor that offers robust security measures and compliance with privacy regulations. |
- Access to high-quality data: AI agents are only as effective as the data they rely on. Incomplete, outdated, or biased datasets can lead to inaccurate results, mistakes, and flawed decisions. Businesses need to make sure their agents have access to high-quality, relevant, and complete data to perform reliably.
- Complex implementation and integration: Deploying agents often requires specialized expertise in machine learning techniques and AI system design. Customizing agents to meet specific business requirements and integrating them with legacy systems, CRMs and internal tools can be challenging. A simple remedy to this challenge is choosing a vendor, such as Creatio, that natively integrates AI agents into their system, significantly accelerating time to value.
- Ethical concerns and bias: AI agents learn from the data they are given. If that data includes existing societal or historical biases, the agent may accidentally repeat or even amplify them in its decisions (e.g., biased lending decisions, unfair hiring recommendations). To mitigate this risk, businesses should implement strong governance policies and responsible AI practices into their development and review processes.
- Lack of transparency (the black box problem): Many advanced AI models, particularly those based on deep learning algorithms, can function as “black boxes”, making it difficult to trace how a decision was made. This lack of transparency can erode trust and create compliance risks, particularly in regulated sectors. To remedy this issue, businesses should carefully evaluate AI agents available on the market and choose the one that provides maximum transparency.
- Security and privacy risks: As AI agents handle and process vast amounts of sensitive business and customer data, they become potential targets for cyber threats. To protect sensitive information and maintain customer trust, businesses should find an AI agent vendor that provides robust security measures, such as data encryption, secure access controls, and compliance with stringent data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
Creatio’s AI Agents - Enhancing Human Capabilities with Role-Based Agents
Creatio is an agentic СRM & workflow platform with no-code and AI at its core, providing powerful AI agents and autonomous banking agents that help organizations automate processes, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency.
Creatio’s agentic platform enables organizations to deploy specialized AI agents that support a wide range of business functions, such as customer service, sales, marketing, and operational workflows. These agents can analyze data, coordinate tasks, communicate with users, and take action across CRM and enterprise systems to automate complex workflows.
AI agents automate routine work and recommend next steps in real time, enabling users to spend more time with customers and focus on strategic tasks. They autonomously deliver contextual insights and directly prioritize and assists with daily tasks. Additionally, AI agents are embedded into the productivity tools you already use, such as MS Outlook and Teams, to surface important information and increase productivity.
Creatio’s role-based AI agents are designed for specific jobs within sales, marketing, and customer service departments:
- Sales teams can use Sales Agents to automate preparation, personalize outreach, and close deals faster with tools that intelligently anticipate needs, produce accurate forecasts, and suggest next-best actions. They can also deploy role-based AI agents to enrich accounts with third-party data, automate quoting, and streamline approvals, documentation, and order fulfillment.
- Marketing teams can leverage Marketing Agents to scale content creation and campaign execution. Role-based agents for marketers can segment the audience, build and coordinate omnichannel campaigns, personalize content, and continuously monitor and improve campaign performance.
- Service teams using Service Agents can deliver faster, more accurate resolutions by leveraging AI to create, prioritize, and summarize cases, extract insights, suggest actions, and streamline communication across channels.
For financial institutions, Creatio provides autonomous banking agents that automate key banking processes by analyzing data, executing workflows, and coordinating tasks across systems with minimal human workers' intervention. These agents are focused on improving revenue generation and operational excellence:
- Revenue Generation Agents include referral, renewal, and retention agents that generate new business and retain existing customers.
- Operational Excellence Agents include customer onboarding, loan preparation, and loan servicing agents that significantly decrease operational costs and increase customer experience
Additionally, business users can create new agents by visually composing skills, workflows, and knowledge in the No-Code Agent Builder, without needing technical expertise. This innovative functionality combines no-code technology with AI capabilities, empowering non-technical users to build AI agents tailored to their unique needs and tasks.
Behind Creatio’s AI agents is Creatio.ai, a powerful AI architecture that delivers a robust set of the latest capabilities. Creatio.ai combines all key AI patterns, including predictive, agentic, and generative AI, helping businesses reduce operational inefficiencies, make smarter decisions, and achieve powerful productivity gains.
Key features of Creatio.ai include:
- AI native architecture combines all key AI patterns into a cohesive and simple architecture, enabling seamless deployment and orchestration of intelligent automation across the enterprise.
- Role-based agents designed around specific business functions, ensuring contextual relevance, clear responsibilities, and alignment with organizational workflows.
- Autonomous banking agents focused on supporting financial institutions with intelligent automation to increase revenue, reduce operational costs, and deliver personalized financial services at scale.
- Embedded agents available directly within everyday productivity tools such as Outlook, Teams, Zoom, and calendars, enabling users to access AI capabilities without switching environments.
- AI Command Center enables users to view and securely manage all AI agents in one place.
- No-code agent builder allows non-technical users to create and deploy new AI agents without writing any code
- AI trust & governance framework ensures secure, compliant, and transparent AI operations through human-in-the-loop controls, monitoring, and policy enforcement.
Creatio.ai is secure, transparent, and governed by responsible practices. It provides enterprise-grade data privacy and security features designed to meet the highest standards of privacy and compliance. By incorporating a human-in-the-loop approach, Creatio.ai ensures that AI decisions are guided by human oversight, enhancing accountability and trust.
What Sets Creatio Apart From Other Vendors in the Market?
Many vendors position their AI agents as workforce substitutes, suggesting they are going to replace human employees. In contrast, Creatio takes a fundamentally different approach, one that views AI agents as digital teammates designed to augment, not replace, human intelligence.
At Creatio, we believe the true power of AI lies in collaboration. Our AI agents are designed to work alongside individuals and teams, supporting them in automating repetitive tasks, providing intelligent recommendations, and enabling faster, more informed decisions. This human-centric philosophy fosters trust, transparency, and broader adoption. It ensures that users feel empowered, not displaced, and are more likely to engage with AI-powered tools.
Creatio’s approach is delivering proven results, with its agentic platform driving measurable business outcomes across industries. Independent Public Sector research shows that government organizations using Creatio can deliver projects 88% faster and increase productivity by 41% through AI-driven document validation and automated governance workflows. Additionally, the Financial Services case study found that financial institutions can deploy new workflows up to 70% faster and reduce application management costs by around 30% within the first year.
Unlike many vendors that treat AI as a premium add-on, Creatio includes these innovations as part of its core: no extra licenses, no hidden fees, and no integration headaches. This approach ensures every organization can achieve maximum AI adoption across teams, without barriers or complexity.

While others are still offering fragmented AI products and complex pricing models, we’ve taken a different path. We offer one platform, one experience, and one clear route to accelerated AI adoption and realizing real business value.
In a market where others may promise automation at the cost of human roles, Creatio delivers responsible innovation that drives efficiency, supports creativity, and values human expertise.
Summary
Unlike traditional automation tools or chatbots, modern AI agents can analyze context, access external systems, perform tasks, and continuously improve their performance through memory and learning. Organizations increasingly use a range of AI solutions, from simple task agents to collaborative multi-agent systems, to automate frontline processes, enhance customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency.
Agentic platforms such as Creatio make it easier to design, deploy, and manage AI agents at scale with natural language and visual components. With built-in governance, integrations, and orchestration capabilities, businesses can safely adopt AI agents and drive measurable outcomes across sales, service, marketing, and operations.





















































