-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
AI Governance - Why Responsible AI Oversight Is Essential
Updated on
September 12, 2025
12 min read
Deploy AI Safely with Creatio

Artificial intelligence is reshaping the way organizations operate, unlocking new levels of efficiency and innovation. But alongside these opportunities come challenges and questions about trust, accountability, and responsible use. That’s where AI governance comes in, providing frameworks and safeguards that ensure AI is fair, transparent, and aligned with human values.
In this article, we’ll explore what AI governance is, why it matters, the principles behind it, and how businesses can put it into practice.
Key Takeaways
- AI governance is essential for trust and adoption - it ensures that AI systems are safe, fair, and transparent.
- Core principles guide responsible AI - transparency, accountability, and human oversight are guiding AI governance alongside regional and industry-specific regulations.
- Governance creates business value - it builds customer trust, supports innovation, and strengthens long-term competitiveness.
- Implementation is practical and achievable - With the right processes in place, organizations can embed governance into daily operations.
What is AI Governance?
AI governance is a set of rules, policies, processes, and practices that guide the responsible development, deployment, and oversight of artificial intelligence systems. It ensures that AI technologies are designed and used ethically and transparently, aligning with human values.
AI governance practices specifically address the unique challenges posed by AI: the potential for bias and hallucinations, data privacy concerns, and the lack of decision explainability. A comprehensive AI governance framework typically includes:
- Ethical considerations and standards: Guidelines such as fairness, transparency, and respect for human rights.
- Risk management processes: Identifying and mitigating risks like bias and misinformation.
- Accountability structures: Assigning responsibility for AI decisions, whether within organizations or at a regulatory level.
- Compliance mechanisms: Ensuring adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards related to AI.
Why is AI Governance Important?
With the current constraints and imperfections of AI models, we can’t allow it to roam free with no supervision. Despite its enormous potential, AI is not flawless. However, according to an EY study, AI adoption is significantly higher than AI governance, with over 75% of surveyed C-level executives using Gen AI but only a third with governance frameworks in place. This situation is not ideal, as AI without any supervision can amplify existing biases, generate misleading or harmful outputs, or operate in ways that are opaque even to its creators.
Without structured oversight mechanisms, the risks of unexpected and sometimes damaging outcomes grow significantly. Air Canada learnt this lesson the hard way when it had to settle a dispute with a customer in court after their AI-powered chatbot provided misleading information.
Here’s why responsible AI governance is so important:
Protecting individuals and society
Poorly governed AI can result in discrimination, privacy violations, or harmful decisions that hit vulnerable groups the hardest. For example, in the financial sector, AI models used for credit scoring or loan approvals have at times reflected historical biases. This can mean that loan applicants from certain neighborhoods or demographic groups are unfairly denied, even when they meet the financial requirements.
AI governance helps prevent these issues by requiring regular audits, bias testing, and clear accountability. With the right safeguards in place, organizations can ensure they are protecting people’s rights and safety.
Building trust and adoption
Even though AI is being adopted rapidly, many people still feel uneasy about it. KPMG’s study shows that while over 60% of people use AI regularly, less than half actually trust it.
This gap is often referred to as AI anxiety, the uncertainty and fear of using something that feels like a “black box.” Most users don’t fully understand how AI models make decisions, and that lack of clarity fuels hesitation.
Strong governance helps bridge that gap. By making AI systems more transparent, showing how decisions are made, and implementing accountability measures, organizations can reduce fear and build confidence. People don’t need to know every technical detail, but they do need assurance that AI is being used responsibly, fairly, and with safeguards in place.
Managing risks and compliance
Governments around the world are starting to roll out new rules and standards for AI, like the EU AI Act or the U.S. AI Bill of Rights. If companies don’t put proper governance in place, they risk falling behind or even getting hit with steep fines - up to 7% of global annual turnover in the EU! Having a strong AI governance framework helps organizations stay on top of these regulations, avoid unnecessary risks, and be ready for whatever new laws come next.
The State of AI Agents & No-Code
Learn how 560+ leaders across the world use AI and no-code to drive innovation today
Key Principles of AI Governance
Responsible AI governance is built upon a set of guiding principles that ensure artificial intelligence is developed and applied responsibly. While the specific frameworks may vary across regions and organizations, most governance approaches converge on a few core principles:
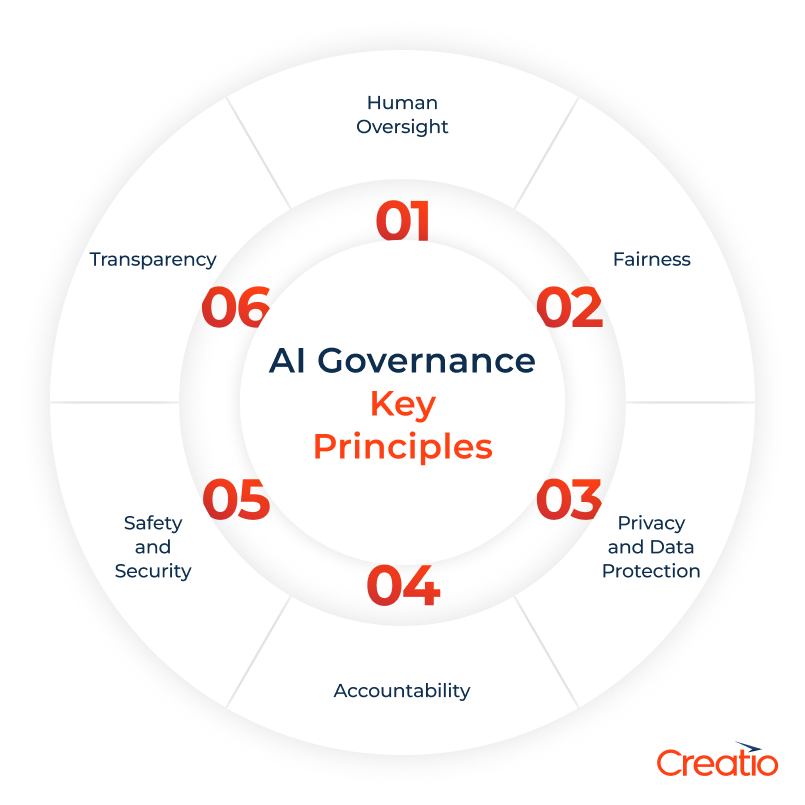
1. Transparency
AI systems should be understandable to users, stakeholders, and regulators. Transparency involves documenting how models are trained, what data they use, and the logic behind their outputs. Users should have easy access to information about the decision pathways and reasoning to assess how AI reached its conclusions and whether it was correct.
2. Fairness
Bias and fairness are two of the most pressing challenges that businesses face when using AI. Ensuring fairness means AI should not discriminate based on race, gender, age, or other protected characteristics, and should promote equitable outcomes across diverse populations.
AI Governance puts in place proactive measures to identify, mitigate, and monitor unfair biases in algorithms.
3. Accountability
Clear lines of responsibility are essential, especially when something “goes wrong”. Organizations must designate who is accountable for the design, deployment, and consequences of AI systems to avoid blurred responsibility and decision-making delays.
Accountability mechanisms also include audit trails, monitoring processes, and the ability to intervene or shut down systems when necessary.
4. Privacy and data protection
Since AI relies on vast amounts of corporate and personal data to train and operate, protecting sensitive information is paramount. Governance frameworks ensure compliance with data protection laws, limit unnecessary data collection, prevent proprietary data sharing, and apply techniques like anonymization to safeguard private data.
5. Safety and security
AI systems must also be protected from malicious attacks. Without proper safeguards, they can become targets for data breaches, hacking attempts, or unauthorized access.
Responsible use of AI requires strong security measures, such as multi-layer encryption, role-based access controls, and continuous monitoring, to ensure AI systems are protected against evolving threats.
6. Human oversight
At the end of the day, critical decisions should remain in the hands of humans. Governance highlights the idea of keeping a human in the loop, meaning AI should augment human capabilities, not take over completely, especially when it comes to crucial business decisions.

At Creatio, we believe the future of automation lies in humans and AI working side by side. Our approach ensures that every AI decision is guided by human oversight, backed by governance, and uncompromising data security.
In practice, this approach makes sure humans stay involved at the important points in a process, stepping in to review, decide, or intervene whenever it really matters.
Standards of AI Governance
AI governance is shaped by a growing web of international and industry standards, regulations, and best practices. These standards set the benchmarks for how organizations should design, deploy, and monitor AI responsibly.
While they vary across regions and industries, several key categories stand out:
1. Global and regional AI regulations
Currently, there's no one global AI governance framework; however, many governments worldwide are actively passing legislation to ensure the responsible use of AI in their region. The EU AI Act, for example, classifies AI systems by risk level and places strict requirements on high-risk applications in the European Union.
In the U.S., while there’s no single nationwide law, initiatives like the AI Bill of Rights outline principles of fairness and accountability, and states such as California are already tightening AI-related rules.
Other countries, such as Canada (AIDA), Singapore (National AI Strategy), and South Korea (Basic Act), have also introduced their own frameworks, signaling a global shift toward stricter oversight.
2. Industry-specific standards
Beyond broad rules, many industries must comply with AI regulations designed specifically for them:
- Healthcare (HIPAA in the U.S.): Hospitals using AI for diagnostics must ensure patient data is anonymized and securely handled. For instance, an AI model analyzing MRI scans cannot retain identifiable patient data outside of HIPAA-compliant systems.
- Finance (FINRA, Basel III): Banks adopting AI for fraud detection or credit scoring must meet transparency and risk-management standards. A bank using machine learning to approve mortgages needs to demonstrate that its system isn’t unintentionally discriminating based on zip codes or demographics.
- Data Privacy (GDPR in the EU, CCPA in California): A retailer using AI-powered chatbots must keep customer data secure and be upfront about any personal information being collected. Customers should also have the clear option to opt out or request that their data be deleted.
3. Intergovernmental standards and ethical guidelines
International organizations are also shaping governance through voluntary but influential standards that provide a global framework for policymakers and AI developers.
The OECD AI Principles and UNESCO’s AI Ethics Recommendation emphasize values such as transparency, fairness, accountability, and respect for human rights. They advocate for an AI ecosystem that is human-centric, respects democratic values and human rights, and promotes inclusive growth and sustainable development.
On the technical side, the ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42 committee is working on global standards for AI quality, trustworthiness, and risk management. Many companies adopt these voluntarily to signal responsibility and prepare for future regulations.
4. Organizational best practices
Finally, good governance goes beyond top-down regulations. Many organizations set up their own AI ethics boards or responsible AI teams to evaluate new projects.
For example, Google has published its AI Principles to guide responsible AI development.
We believe our approach to AI must be both bold and responsible. Bold in rapidly innovating and deploying AI in groundbreaking products used by and benefiting people everywhere [...] and responsible in developing and deploying AI that addresses both user needs and broader responsibilities, while safeguarding user safety, security, and privacy. - Google AI Principles
On a smaller scale, startups often adopt bias testing protocols or third-party audits to reassure investors and customers that their AI tools can be trusted.
Core Business Benefits of Implementing AI Governance
AI governance isn’t just about meeting legal requirements - it’s also a smart bu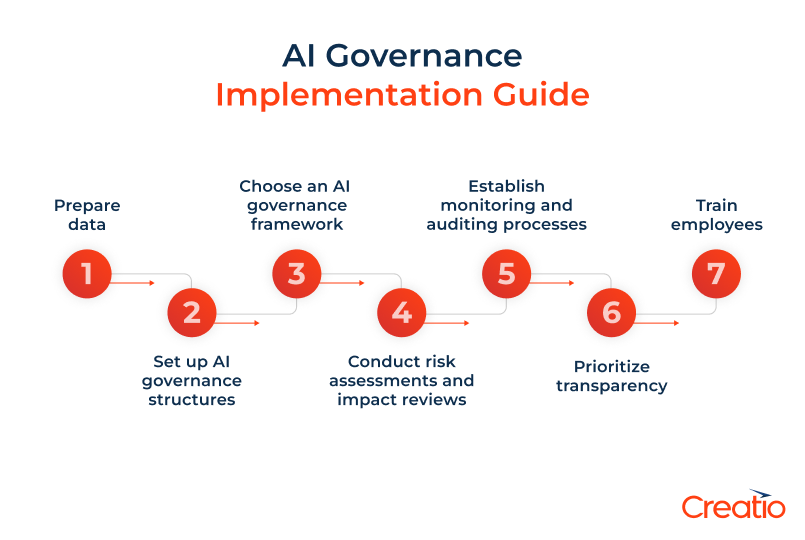 siness strategy. By putting the right guardrails in place, organizations can reduce risks, build customer trust, and protect their reputation.
siness strategy. By putting the right guardrails in place, organizations can reduce risks, build customer trust, and protect their reputation.
Here’s what organizations can achieve with the right AI governance policies in place:
- Improve the reliability of AI outcomes - AI governance improves AI-generated outcomes by promoting the use of robust, unbiased, and high-quality data.
- Reduce compliance risks - by establishing clear guidelines and standards that align AI systems with legal and regulatory requirements, organizations can ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties.
- Ensure explainability - transparent AI systems enable organizations to understand how AI-driven decisions are made, which facilitates the assessment and implementation.
- Promote secure collaboration - AI governance outlines clear protocols for using data and AI across the organization.
- Build trust among stakeholders - AI governance helps reduce fears and uncertainties related to AI deployment. This helps scale AI programs efficiently and accelerate organization-wide adoption.
How Companies Can Implement AI Governance in Practice
Having principles and standards is one thing but putting them into practice is another. For organizations, effective AI governance means creating clear structures, processes, and accountability measures that guide how AI is built, deployed, and monitored over time.
1. Start with data preparation
Data is the lifeblood of any AI system, and proper governance should begin here. Companies need to ensure that the data feeding their models is accurate, representative, and collected lawfully. This means cleaning and standardizing datasets, documenting their sources, and checking for hidden biases that could skew results.
2. Set up AI governance structures
Organizations at the forefront of AI adoption are using a centralized approach by establishing AI centers of excellence (AI COE) to oversee decision-making. AI COE brings together leaders from legal, compliance, technology, and business units to evaluate risks and ensure AI projects align with company values.
3. Choose an AI governance framework
As we mentioned before, there isn’t one specific framework, guideline, or law that all AI-deploying and developing organizations should use. Because regulations differ across countries, regions, and industries, companies need to choose the AI governance framework that best suits their needs and fits into their broader compliance and risk management strategy.
The right governance model should not only align with legal requirements but also reflect the company’s values, industry standards, and commitment to responsible AI practices.
4. Conduct risk assessments and impact reviews
Before deploying AI, organizations should assess potential risks - bias, security vulnerabilities, legal exposure, or reputational harm. Tools like AI impact assessments are gaining traction, especially in regions like the EU.
At the same time, organizations should allow some flexibility and use real-time risk classification and tiering. This approach allows them to apply stronger controls where risks are highest (e.g., personal identifiable information, protected health information, autonomous actions) and lighter controls where speed of innovation is critical.
5. Establish monitoring and auditing processes
Continuous monitoring helps catch issues like model drift, bias re-emergence, or unexpected outcomes.
To ensure proper monitoring and auditing, organizations should implement:
- Dashboards with real-time updates
- Intuitive governance metrics
- Automated detection systems
- Performance alerts
- Comprehensive logs and audit trails
Organizations can leverage governance AI agents to further simplify monitoring and auditing. These agents autonomously track evolving risks, regulatory changes, and system performance. They can automatically detect issues, trigger alerts, and recommend controls to keep operations compliant and secure.
6. Prioritize transparency
Transparency doesn’t mean exposing every line of code — but it does mean documenting how AI systems work, what data they rely on, and what safeguards are in place.
Organizations should explain their AI systems in plain language to regulators, customers, and employees. This will reduce anxiety and help people trust the technology.
7. Train employees
Effective AI governance requires organization-wide awareness, not just policies written on paper. Training employees on responsible AI practices helps prevent misuse, reduce risks, and build confidence in using the technology.
This training should go beyond technical teams. Business users, managers, and executives need to understand how AI works, where its limitations lie, and when human oversight is essential to ensure AI governance is actively practiced.
Creatio AI Governance
Creatio takes a comprehensive approach to AI governance, ensuring that organizations can embrace AI-driven automation without sacrificing security, compliance, or control. At the heart of this approach is a secure and flexible AI architecture built on transparency, accountability, and strict data protection.
In Creatio’s agentic platform, security is built in from the ground up. AI agents follow a zero-trust security model and role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring that confidential data is never disclosed to unauthorized users. Creatio is also fully aligned with global data protection laws, including GDPR, PII regulations, and enterprise security standards. Audit trails and policy-based AI controls provide an additional layer of oversight, allowing businesses to define rules for AI behavior, enforce restrictions, and maintain detailed compliance reporting to ensure regulatory alignment.
Creatio’s governance model also emphasizes the importance of human oversight. AI agents are designed to support, not replace, people, adopting a “human-in-the-loop” approach that keeps critical decisions in human hands. To support this approach, Creatio ensures that AI decisions are transparent, fair, and explainable, helping users understand how AI reaches its conclusions with full visibility into AI logic, data sources, and reasoning.
Creatio's strong AI governance practices enable organizations to leverage the power of AI while ensuring that it remains safe, responsible, and aligned with organizational values and regulatory requirements.
Governing AI for a Responsible Future
AI is woven into the way we work, make decisions, and live our daily lives. But with its growing influence comes equally growing responsibility. Poorly managed AI can lead to bias, privacy breaches, and harmful outcomes, while well-governed AI can build trust, drive innovation, and unlock enormous social and economic benefits.
Responsible AI governance is more than compliance with laws and industry standards; it’s about earning trust. By implementing safeguards, maintaining transparency, and keeping humans involved in decision-making, organizations can turn fear and uncertainty into confidence and widespread adoption.
With the right AI systems, like Creatio, governance becomes straightforward. Our platform is designed with security, compliance, and trust at its core, handling the heavy lifting of governance so businesses can stay focused on driving innovation and growth.






















































