-
No-code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code AI-native platform to build applications faster
Discover

-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM


-
Industries

- Customers
-
Partners

-
About

Generative AI Agents: Capabilities, Advantages and Principal Use Cases
Updated on
August 20, 2025
12 min read
Transform Your Business with AI Agents. Get Creatio

Since the rise of ChatGPT, generative AI (GenAI) has redefined the potential of artificial intelligence (AI), reshaping the way organisations synthesise information, generate content, and engage with AI systems using natural language. According to McKinsey’s estimations, GenAI holds the potential to deliver between $2.6 and $4.4 trillion (~£2.05 to £3.48 trillion) in additional value, over and above that offered by traditional AI technologies.
The next wave of innovation in generative AI extends beyond basic question-answering and content creation, ushering in the era of autonomous GenAI agents. These advanced systems are capable of managing and executing complex, multistep workflows, enhanced by generative AI capabilities.
This article explores what generative AI agents are, how they function, and the transformative potential they hold for modern businesses.
Essential Insights:
- Generative AI agents stand apart from other AI agents by combining autonomous, action-driven capabilities with advanced content generation.
- GenAI agents accomplish tasks by planning, using both short- and long-term memory, and interacting with other tools.
- The principal advantages of generative AI agents include enhanced creativity, more intelligent decision-making, and improved overall productivity.
- To fully harness the capabilities of generative AI agents, businesses should document key processes as structured workflows, ensure smooth integration with existing data and infrastructure, and implement human-in-the-loop oversight.
- Creatio enables businesses to deploy role-based AI agents tailored to specific job functions and industries, while also offering tools to develop custom agents suited to unique workflows and requirements.
What are Generative AI Agents?
A generative AI agent refers to an advanced AI system that merges the capabilities of generative AI, such as producing text, images, or code, with autonomous, goal-oriented behaviour, often described as agentic functionality. These agents do far more than merely generate content. They are capable of analysing inputs, reasoning through objectives, and taking independent actions across systems, all without the need for constant human intervention.
Such agents are particularly well-suited to automating complex workflows and accelerating operational efficiency. By making sequential decisions, adapting to real-time context, and continuously learning from data, generative AI agents can perform multistep tasks across a wide range of industries, including finance, technology, manufacturing, public sector, and beyond.
To illustrate, a generative AI agent might automatically create and send personalised marketing emails, generate sales quotes, design branded content, or prepare your team for an upcoming client meeting, all without direct human involvement.
How Do Generative AI Agents Operate?
At their core, generative AI agents are driven by advanced machine learning (ML) models trained on vast datasets. These models are designed to understand context, generate tailored content, and take action. Their capabilities are further enhanced through the use of complementary technologies, such as natural language processing (NLP) for interpreting text, computer vision for analysing visuals, and decision-making algorithms that enable planning and execution of tasks.
This combination allows generative AI agents to operate independently, managing multistep workflows and adapting to real-time changes. To function autonomously, these agents rely on four fundamental attributes:
- Planning: Generative AI agents are capable of taking high-level objectives, such as “produce a monthly sales report”, and breaking them down into manageable steps. They create a structured plan, determine the most effective approach, and execute it step by step, rather than simply following predefined rules.
- Memory: These “agentic” systems are design to retain knowledge of past interactions, decisions, and outcomes. By leveraging short-term and long-term memory, they maintain consistency, avoid unnecessary repetition, and evolve over time based on feedback and context.
- Tool Use: GenAI agents interact directly with a range of business tools, whether CRMs, industry-specific tools, or APIs. They retrieve data, update records, initiate actions, and integrate seamlessly with enterprise systems to perform tasks automatically.
- Generative AI Capabilities: What distinguishes these agents apart is their creative capacity. They can generate emails, reports, summaries, presentations, and even code. With native NLP and computer vision capabilities, they comprehend instructions in natural language, analyse varied inputs, and produce tailored outputs on demand.
Taken together, these capabilities enable generative AI agents not only to think and create, but also to act. In essence, they operate as intelligent digital collaborators.
A Real-World Example of Generative AI Agent in Action
Consider a scenario in which a Chief Sales Officer request a report from a GenAI, seeking to identify the top-performing sales representatives from the previous month. At first glance, the interaction between the agent and the human may appear straightforward:
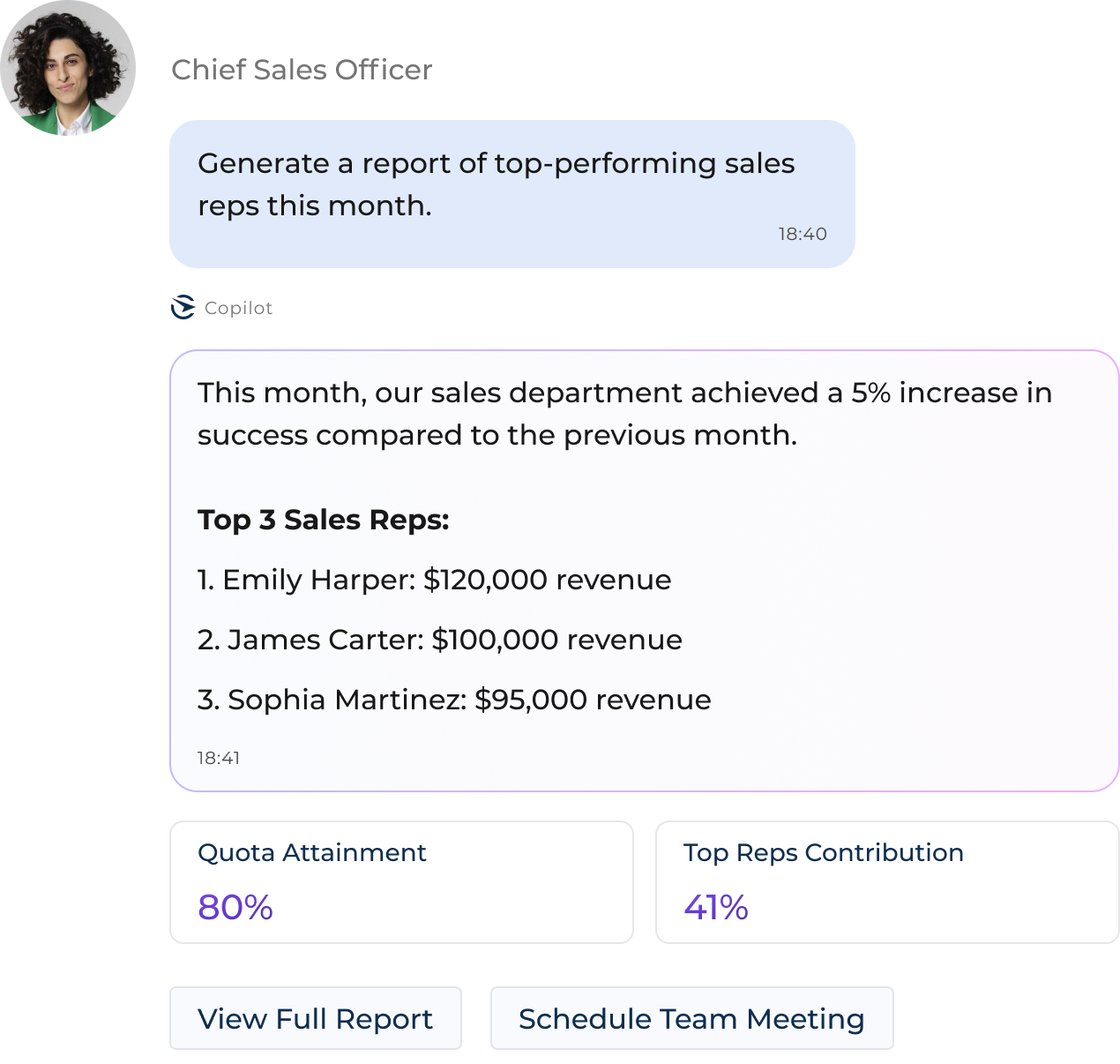
Example of a user engaging with a Generative AI agent
However, behind the scenes, the agent is executing a sophisticated sequence of reasoning and actions:
- Interprets the request using NLP.
- Formulates a plan to gather the necessary data (e.g., accessing the CRM and reviewing individual sales performance).
- Connects to the CRM to retrieve the relevant sales data.
- Retains contextual information (such as the time period) in its memory.
- Generates a clear summary, highlighting the top three performers based on revenue.
By chaining reasoning with actions and dynamically responding to insights, generative AI agents execute tasks at scale, keeping outputs accurate, relevant, and also fully aligned with business objectives.
Types of Generative AI Agents
Generative AI agents may be classified in various ways. For instance, they are frequently grouped according to modality, such as text-only, visual, or multimodal, or by their intended use case, which encompasses a vast range of business applications.
However, a more practical and accessible framework has been proposed by Patrick Marlow, Google’s Generative AI Agents evangelist, who divides them into two primary categories:
- Conversational Agents – designed to engage directly with humans, responding to queries in natural language. They retrieve information and assist with a range of tasks or transactions. The common examples include AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and helpdesk agents that handle Q&A functions, guide users through processes, or automate front-end requests.
- Workflow Agents – operate independently in the system’s background, with minimal or no human involvement. They are triggered by system events, such as entry of new data, time-based conditions, or changes in status, and used to carry out more complex, automated tasks. Examples include AI agents that route leads, prepare reports, and initiate approvals across business systems.
What Distinguishes Generative AI Agents from Other AI Models?
The fundamental distinction of generative AI agents lies in their unique capacity to reason autonomously and generate context-specific content with precision. Unlike more conventional AI systems, these agents are capable of creating, adapting, and executing multistep workflows, making them particularly well-suited to complex, dynamic, and open-ended scenarios.
Several notable characteristics differentiate generative AI agents:
- Content generation, enabling them to function as problem-solvers.
- Enhanced autonomy, allowing GenAI agents to operate independently in real-time, often with significantly reduced human intervention.
- In-depth context understanding, which supports more human-like, relevant, and responsive interactions.
- Adaptability, enabling agents to learn continuously, improve their performance through ongoing data and interactions, and adjust in line with evolving circumstances.
Defining Characteristics of Generative AI Agents
According to Deloitte’s State of Generative AI in the Enterprise survey, 25% of organisations currently utilising generative AI intend to launch agentic AI pilots or proofs of concept in 2025. That figure is expected to double by 2027, highlighting a swift and growing interest in agentic AI applications across the enterprise landscape.
The surge in the adoption of AI agents is driven by a powerful set of foundational capabilities, which are outlined below.
1. Generative Capabilities and Creativity
A defining feature of generative AI agents lies in the ability to create unique content, such as text, images, summaries, emails, code, and reports, precisely tailored to specific tasks and business objectives. These agents are capable of adapting output in real time, responding to evolving contexts, and drawing insights from extensive sets of both structured and unstructured data. Such versatility renders them highly valuable across a wide arrays of industries and use cases.
2. Autonomy and Context Awareness
Generative AI agents function autonomously, capable of breaking down goals, making decisions, and continuously adjusting actions based on observed results. Rather like a capable and trusted human assistant, they can identify and resolve issues, analyse outcomes, and adapt their approach dynamically. Moreover, they remain contextually aware at all times, taking into account factors such as business objectives, previous actions, and live data, thereby ensuing accurate, purpose-driven responses.
3. Natural Language Understanding and Instruction
Generative AI agents are generally directed through straightforward, natural language prompts, which eliminates the need for intricate coding, thereby making them accessible for non-technical teams. Their capacity for engaging in multi-turn, human-like conversations enables smooth integration into routine workflows across various departments.
4. Multistep Task Execution
Owing to their agentic architecture, generative AI agents are capable of managing complex processes from beginning to end. They chain actions such as retrieving data, making decisions, generating content, and executing next steps, creating a seamless reasoning-and-action loop that closely resembles human workflows.
5. Tool and System Integration
Generative AI agents are capable of interacting directly with CRMs, APIs, spreadsheets, databases, and other applications, enabling them to operate effectively across the wider business technology environment. Such integration positions GenAI agents as indispensable tools for managing complex workflows and delivering measurable business outcomes at scale.
Principal Use Cases of Generative AI Agents
The potential of generative AI agents is expanding rapidly, along with their influence across a wide range of industries. As the technology continues to evolve, businesses are seeking innovative ways to harness GenAI agents in areas such as sales, marketing, finance, customer service, and other key operational domains.
Sales
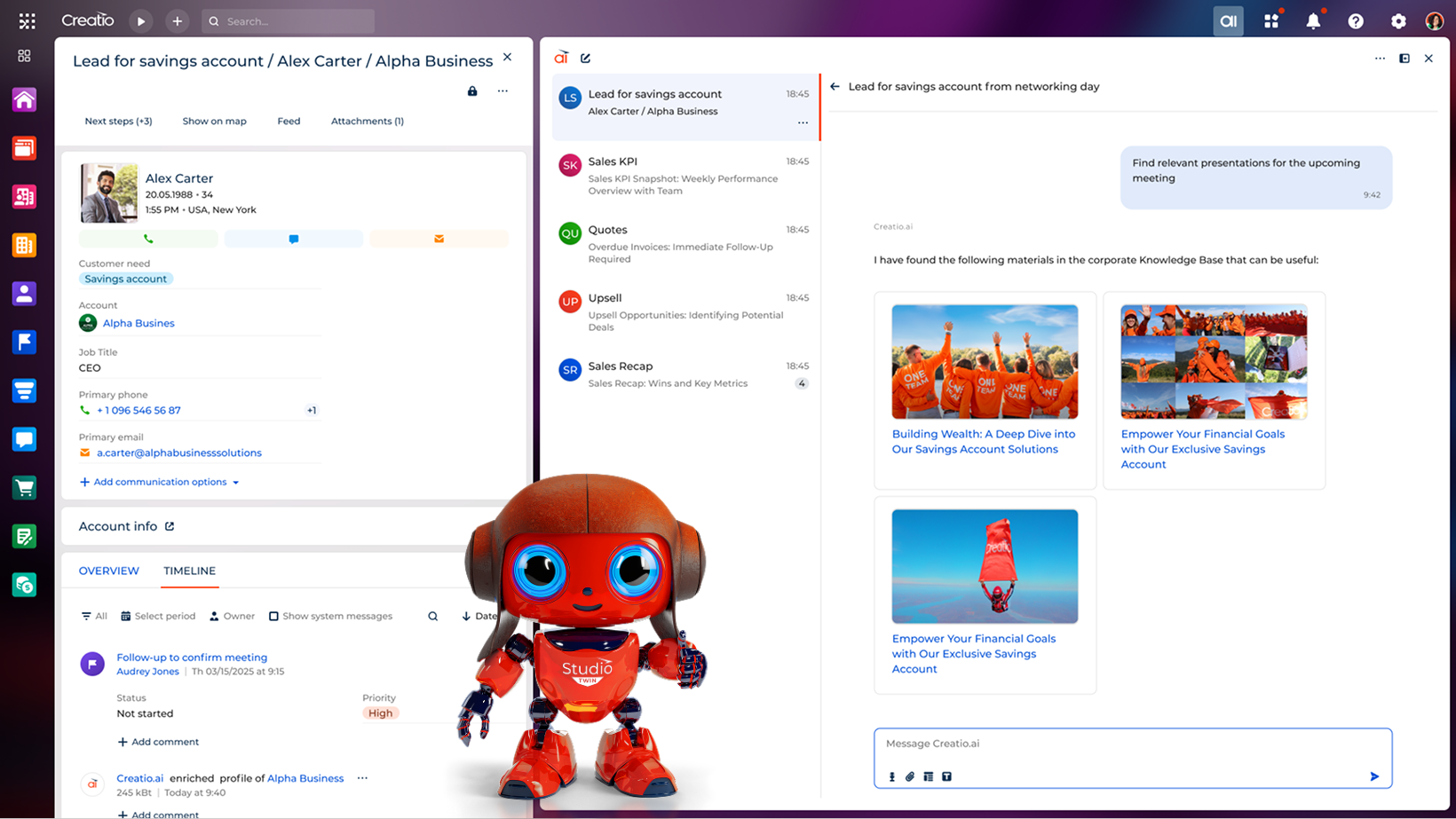
Generative AI agents enhance sales productivity by automating various routine tasks, including creating personalised follow-up emails, compiling meeting summaries, updating customer records, and recommending next-best actions or upsell and cross-sell opportunities. Based on the in-depth analysis of the collected user data and interactions, a GenAI agent can also qualify and route leads in real-time. This not only enhances the effectiveness of sales representatives but also significantly increases the sales revenue.
Examples of sales-oriented GenAI agents:
- Account Research Agent: Gathers essential information on prospects from internal systems and public sources
- Quote Agent: Drafts personalised proposals and pricing documents based on provided inputs
- Meeting Prep Agent: Summarises account history, objectives, and recommended next steps ahead of upcoming calls
- Forecast Agent: Reviews pipeline trends and generates forecast summaries for managers
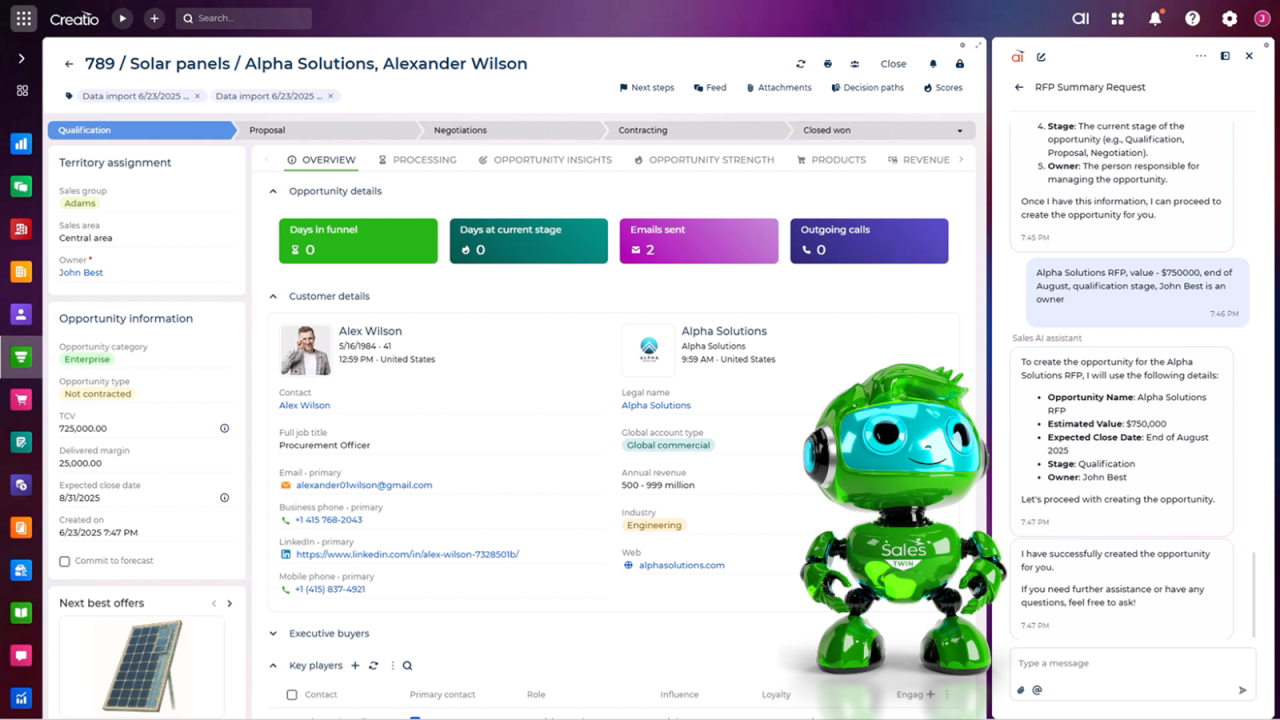
Example of Creatio’s Sales AI Agent
Marketing
In marketing, generative AI agents enhance campaign performance by streamlining execution and improving personalisation at scale. These autonomous systems are capable of creating and localising content assets, such as emails, social posts, and landing pages, which are tailored to specific audiences and campaign objectives. By analysing real-time engagement signals alongside historical performance data, they empower marketers to refine targeting, accelerate content generation and gain real-time insights to maximise marketing ROI.
Examples of marketing-oriented GenAI agents:
- Marketing Content Agent: Generates email copy, landing pages, and advertising creatives tailored to specific segments or buyer intent
- Email Generation Agent: Produces highly personalised email content informed by lead behaviour and lifecycle stage
- Lead Scoring Agent: Assesses leads by analysing their responses and behavioural patterns to determine their likelihood of conversion
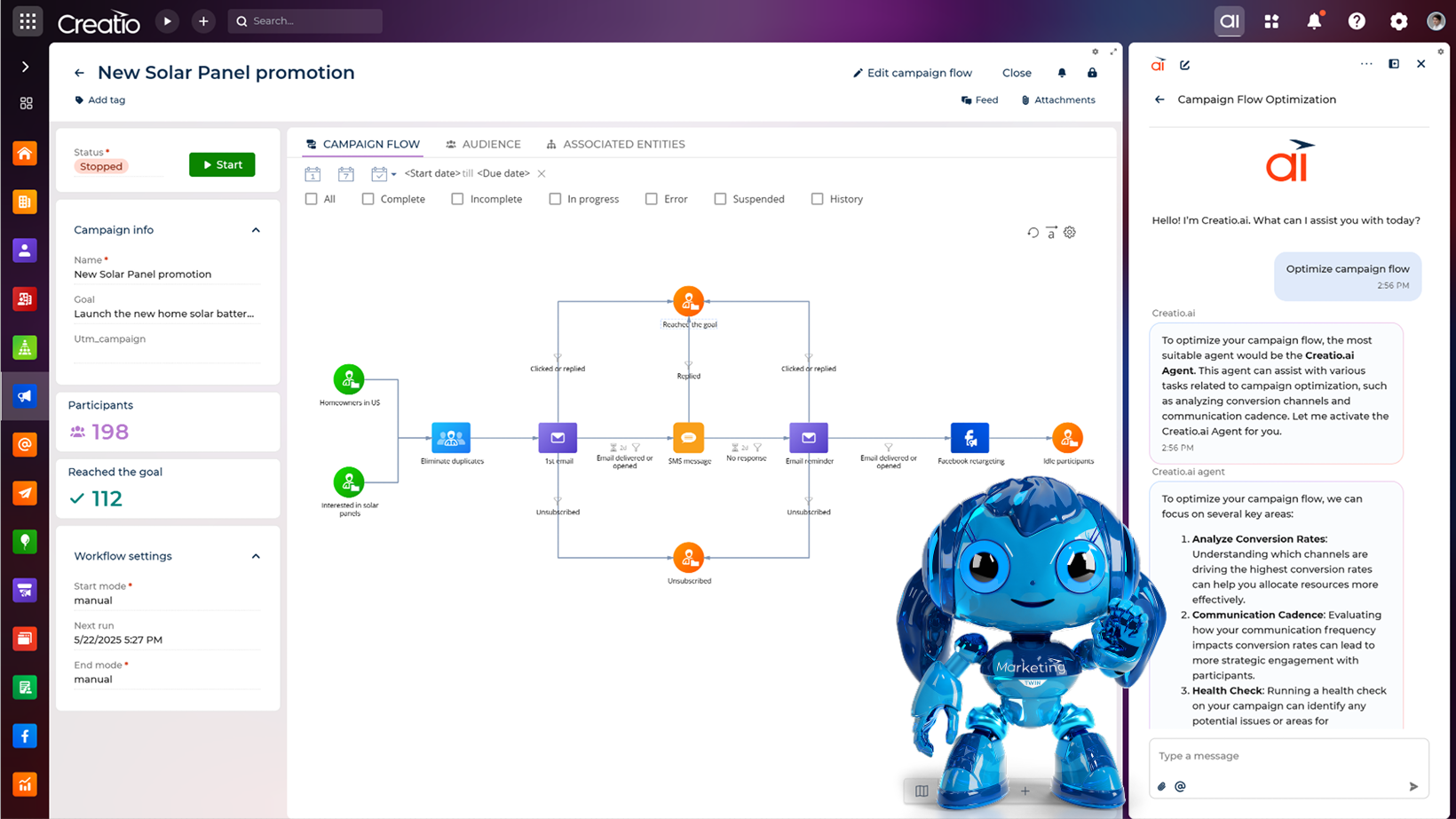
Example of Creatio’s Marketing AI Agent
Customer Service
Generative AI agents are reshaping customer service by automating high-volume interactions, delivering contextual responses, and significantly reducing resolution times. In particular, these agents are capable of producing human-like responses to support tickets and inquiries, as well as summarising lengthy conversation threads and highlighting key issues for escalation. They can also analyse tickets based on intent and priority, and recommend updates to internal knowledge bases to address recurring issues, enabling teams to resolve problems more efficiently and enhance customer satisfaction.
Following the integration of generative AI into its customer service operations, Lenovo has reported a 17% increase in customer satisfaction within just one year.
Examples of service-oriented GenAI agents:
- Customer Support Agent: Automates the handling of tier-1 and tier-2 cases across multiple communication channels
- Knowledge Base Agent: Retrieves, summarises, and presents the most relevant articles or documentation from the internal bases
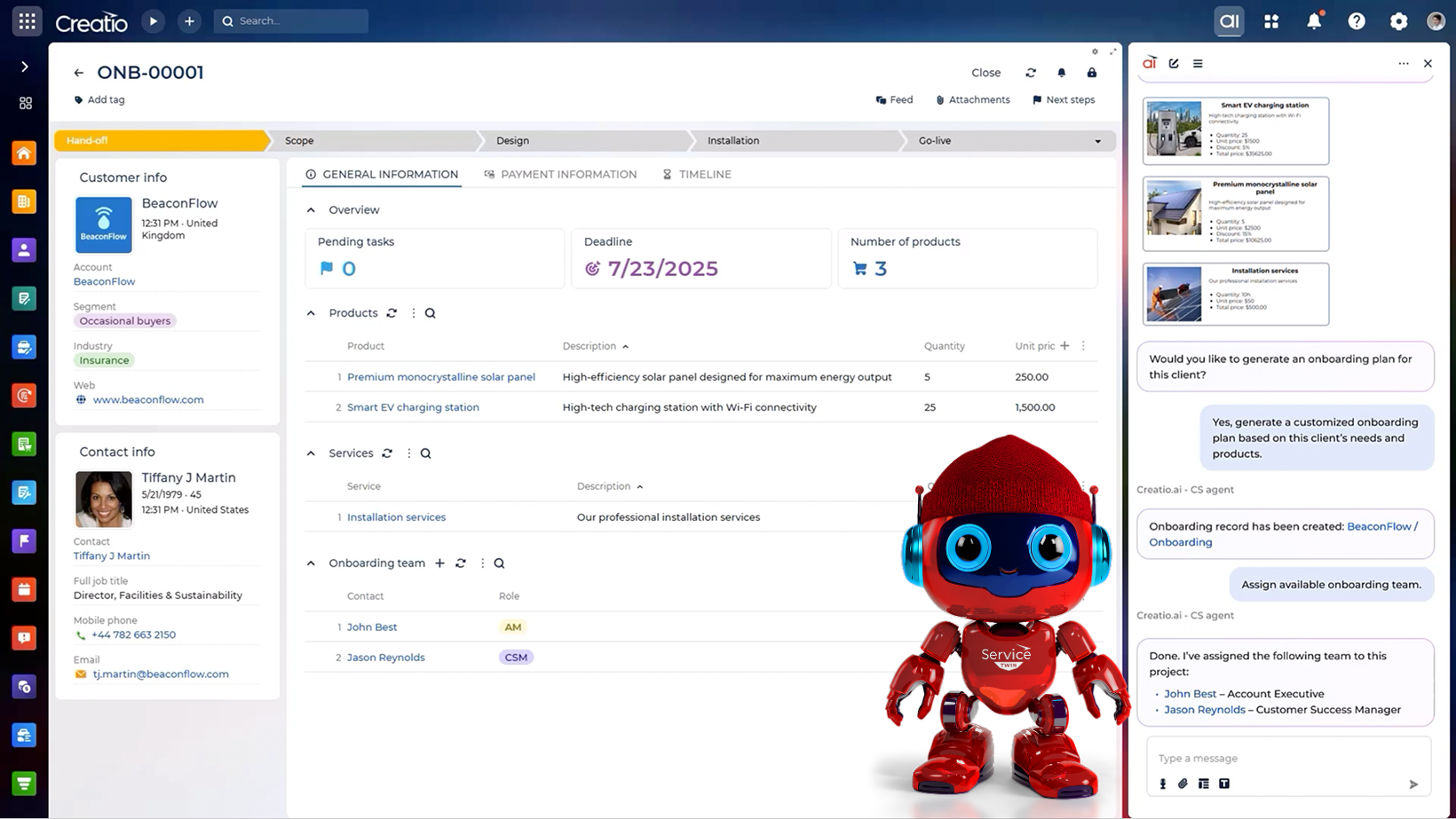
Example of Creatio’s AI Agent for Service
Document and Knowledge Work
Generative AI agents empower teams to simplify and accelerate the creation, organisation, and retrieval of both internal and external documentation. This not only reduces manual effort but also enhances access to essential knowledge assets across the organisation.
Examples of Generative AI Agents:
- Document Drafting Agent: Generates proposals, contracts, and reports based on user inputs and templates
- Knowledge Article Generation Agent: Creates and maintains FAQs, SOPs, and content for internal knowledge bases
Industry-specific Operations and Workflow Automation
GenAI agents can be configured to meet the distinct requirements of industry-specific operations. For instance, they are capable of performing tasks such as claims processing, real-time calculations and data summarisations, as well as automated lead data capture. By integrating tools, teams, and data, these customisable AI-powered agents enable businesses to accelerate execution, minimise manual effort, and ensure consistent outcomes.
According to McKinsey’s projections on the future of generative AI, such agents could reduce the time required to produce credit-risk memos by as much as 20% to 60%.
Common use cases for GenAI agents in operational contexts:
- Generating customer quotations
- Designing campaign workflows
- Creating communication templates
- Providing lead funnel overviews
- Conducting sentiment analysis and generating responses for cases
- Producing activity summaries
These examples illustrate just a few of the many ways generative AI agents are being applied across operational functions.
How Generative AI Agents Add Value to Business
Once implemented, generative AI agents can significantly transform businesses operations by automating, optimising, and scaling core processes. Among the primary advantages are:
- Enhanced creativity. GenAI agents generate content, ideas, and solutions through the use of advanced machine learning models, thereby supporting teams across marketing, design, product development, and other creative tasks.
- More intelligent decision-making. By processing large volumes of both structured and unstructured data, generative AI agents can uncover valuable insights, evaluate potential risks, and enable faster, better-informed decisions.
- Real-time adaptability. GenAI agents respond dynamically to changing inputs, allowing businesses to remain agile and adjust instantly to shifts in customer behaviour, market dynamics, or system changes.
- Increased efficiency and productivity. By taking over repetitive tasks and automating routine workflows, agents enable human teams to concentrate on high-value work.
- Faster process scaling and innovation. AI agents allow businesses to replicate and adapt successful workflows across teams and regions with ease, accelerating time-to-market and experimentation.
- Reduced operational expenses. Through automation, AI agents help businesses minimise manual effort, prevent costly errors, and significantly lower overall expenditure across departments.
Preparing for the “Agentic Future”: How Business Can Embrace GenAI Agents
As organisations move beyond experimentation towards the widespread adoption of generative AI agents, those unprepared risk being left behind. To help businesses fully harness the potential of agentic AI, McKinsey outlines three readiness factors to prioritise :
1. Codify Core Knowledge
In order for AI agents to manage complex tasks efficiently and at scale, organisations must clearly define and document essential processes as structured workflows. Capturing subject matter expertise in natural language further enhances agent training, leading to more efficient and streamlined operations.
2. Modernise Data and IT Systems
To operate efficiently across various workflows, AI agents require seamless access to both data and infrastructure. Organisations should ensure their IT systems environments are equipped to support agent interactions, facilitate continuous feedback, and accommodate new technologies without causing disruption to existing systems.
3. Implement Human-in-the-Loop Oversight
As generative AI agents assume greater levels of autonomy, human validation remains essential. Businesses must define when and how employees should review AI-generated outputs to ensure accuracy, uphold ethical standards, and maintain alignment with business objectives.
Enhance Business Performance with Creatio AI Agents
Generative AI agents are already reshaping the way businesses operate across industries. By automating routine workflows, enhancing creativity, uncovering actionable insights, and enabling intelligent execution at scale, they are becoming essential tools for modern enterprises. Whether you're implementing ready-made agents or building custom solutions tailored to your specific operational needs, Creatio empowers your business to succeed with AI.
Creatio offers both out-of-the-box AI agents and flexibility to create custom AI agents, built upon its AI-native platform, trusted by global enterprises to power intelligent automation at scale. Its no-code tools and composable architecture allow domain experts to automate industry workflows and CRM without writing a line of code. With generative, predictive, and agentic AI embedded at its core, Creatio enables organisations to design fully autonomous agentic workflows or to augment human teams through intelligent collaboration between AI agents and human. The combination of hybrid human-digital talent properly applied in your business allows you to expand and achieve meaningful outcomes.
Built with enterprise-grade security and compliance at its core, Creatio safeguards data privacy and governance at scale, supporting organisations operating within regulated industries.
Pre-built AI agents for sales, marketing, and service are available across Creatio’s CRM solutions. These agents are capable of researching account data, generating quotes, preparing meeting briefs, drafting personalised emails, creating campaign content, producing knowledge base articles, and supporting a variety of other specific processes and workflows. With the No-Code Agent Builder, business users and domain experts can create bespoke AI agents by visually composing agent skills, workflows, and knowledge – without the need for any coding expertise.

