-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
Improve Forecast Accuracy With Creatio AI

Sales forecasting should be the foundation for your company’s business strategy – knowing future revenue allows companies to make more strategic decisions. Undoubtedly, this business strategy can be based on the opinions of your sales executives, as sales forecasts often are. According to the Gartner State of Sales Operations Report, only 45% of sales leaders are confident in their organization’s sales forecasts. Fortunately, there are data-informed ways to increase this confidence.
In this article, we explain various sales forecasting methodologies and give you a guide that guarantees a solid foundation for your company’s operations.
What is Sales Forecasting?
Sales forecasting is the process of predicting your future revenue in a set period of time by estimating how many sales you’ll close in this period. It typically relies on past results to project the success of your sales efforts. Sales forecasts are often shared with company executives and stakeholders. Short-term sales forecasts can also be used internally for Sales to predict the individual results of each account executive.
The two main queries your sales forecasts answer are: how much revenue you can expect and when you can expect it. These reports then become the basis for all the strategic decisions across the company, such as hiring new employees, allocating budgets, developing new pricing models, etc.
Why is Sales Forecasting Important?
Sales forecasts make your business operations more transparent and goal-oriented, enabling you to avoid future overspending or undervaluing your capacity for growth. It brings the following benefits to your organization.
Informed decision-making aimed at growth
Sales forecasting allows you to predict growth in the upcoming period and develop and implement specific measures to boost this growth. On the contrary, if you plan your business strategy without such predictions, you end up unprepared for what's to come. Sales forecasting allows you to avoid overestimating your sales team capacity and thus, it helps to set adequate goals for your sales representatives.
Strategic resource allocation
If you know what revenue you can count on in a certain period, you can assess where to place this revenue. Moreover, sophisticated sales forecasting methods allow you to see correlations between budget planning and profit. For example, it can highlight how your ad spending affects your revenue and enables you to design future budgets accordingly. All in all, it allows you to plan your budget more effectively and secure ROI for all the departments across your organization.
Prepare staff changes
One of the key processes that heavily depends on sales forecasts is hiring. For example, if your sales forecasts highlight growth potential, your organization can start hiring specialists in advance to support those growth projections. On the other hand, unfavorable forecasts may suggest a pause in your recruiting efforts or a restructuring of specific departments.
Cross-department alignment
Sales forecasting concerns many departments, not just sales. Sales forecasts can be used by different teams to change their activities and objectives in accordance with expected revenue. For example, in finance sales forecasts are used to create capacity plans and hiring budgets. In production, they are used to organize production cycles. Supply managers can use them to plan material purchases and production capacity.
Proactive problem solving
Having a sales forecast allows your sales executive to easily notice discrepancies between the predictions and actual results and take course-correcting actions earlier. If your sales team is underperforming compared to predictions, it's a clear sign to examine operations and find the reason behind unsatisfactory results. Sales forecasting helps catch such signs early and point out why exactly your results don’t match your expectations.
Motivational boost for your sales team
By predicting sales and setting clear goals, you give motivation to your sales representatives and encourage them to close deals. Since they get precise numbers they are to achieve, it inspires them to be more productive. You can break down your monthly or quarterly forecast into short-term benchmarks and assign these sales quotas to individual team members. Having such targets will help them track the results and ensure that nobody lags behind.
Let's look at different forecasting methods and see which suits your company and promises the best results.
7 Quintessential Sales Forecasting Methods
The accuracy of sales forecasting relies on the method you choose. Let’s go through various ways to forecast sales revenue and examine their advantages, disadvantages, and when they are most appropriate.
Intuitive forecasting

This is the most basic way to predict sales revenue, yet it's widely used among businesses at different stages. As the name suggests, intuitive sales forecasting relies on the opinion of your sales representatives and leaders to estimate the potential closing rates and revenue for a specific date.
For example, your sales rep may say, "I know that typically it takes us about two months to close a deal. I'm certain that the customer I'm talking to right now will pay X amount, so in two months, I'll close this deal for X amount". This may seem a highly unreliable method based strictly on opinions, but there’s merit to it. While you can't call this method data-informed, the judgment comes from people most knowledgeable about your company's sales activities. If you lack robust data, it can be somewhat mitigated by the abundance of experience your team possesses.
Of course, this method is far from accurate, doesn’t allow for long-term predictions, and is impossible to scale. You'd need to constantly ask all your reps about each of their leads without any feasible way to verify their assumptions. So why use this method? For companies with no data-tracking processes, there may be no other choice. The intuitive method can be a short-term solution while you establish a robust data culture to switch to another method later.
Historical (aka seasonal) forecasting

All you need to do is look at the month, quarter, or year results from the matching time period and assume that you can expect the same revenue going forward.
A leveled-up version of this method adds growth rate to your calculations. For example, you know that the first quarter of last year brought you X revenue, which was 3% higher than a year before. The first quarter of the following year will bring you last quarter’s revenue *3% growth. As you see, this method assumes that market trends, buyer demand, and internal strategy will stay the same. This assumption is pretty unrealistic, so you can’t rely on sales forecasting executed in such a rudimentary way.
However, it's also one of the easiest sales forecasting methods to implement and is more reliable than the intuitive method. All in all, we’d recommend choosing a more sophisticated way to predict sales, granted you have enough historical data to support it. However, always account for seasonality as a factor that influences your predictions.
Opportunity stage forecasting

This method encourages you to consider all the leads at the different stages of your funnel and calculate the success rate for each stage. Based on these calculations, you can assign a probability-to-close rate to each funnel stage. This information combined with the current amount of leads in your funnel is used to predict your profit.
Here’s what it looks like. You assign all the stages of your pipeline a likely-to-close probability expressed in percentages. Let's say you currently have 30 potential deals in your pipeline.
- 5 leads are at the initial call stage and have a 5% probability of closure (based on historical sales data)
- 7 leads are at the qualified stage with a 10% probability
- 7 are at the product demo stage and have a 50% probability
- 9 leads are at the product trial stage and have a 70% probability
To calculate your future revenue, you multiply the amount of money expected from each deal by its stage's probability rate. Let's say a deal at the product trial stage is set to make $1000. We multiply $1000 by 70% and predict the revenue of $700. You might have noticed that a couple of essential factors are left unaddressed, mainly the size and age of opportunity. The size of a deal is an important variable in this sales forecasting method, but there is no method to predict it correctly.
The age of the lead is entirely unaccounted for here. The lead that's been in your pipeline for multiple months is assigned the same value as the one that you got yesterday. The next method on the list improves upon this by adding age of opportunity to calculations.
Length of sales cycle method

This method considers an important factor – the age of an opportunity in your pipeline. The length of sales cycle forecasting calculates different probability rates for your leads, depending on how much time they spend in your funnel. Let's say there are two potential customers at the product trial stage. The previous method would attribute the same likelihood of closing a deal with them. Still, anyone understands that the potential customer who just started the trial and the one who almost finished it have different feasibility for your sales forecasting model.
If you have quality data tracking, this model can also account for the source of your opportunities, not just its seniority. For example, it will differentiate between leads that came through the sign-up form on your website and those you met in person at an industry event. To get accurate results, you must carefully track when opportunities enter your pipeline. That means analyzing marketing and sales data, which can be provided through an enterprise CRM that helps you organize your data and facilitates its exchange between teams. It would be extremely challenging to correctly store and process all this data without automation.
Pipeline forecasting

The pipeline forecasting method considers all the sales metrics at hand: age, type, size, and source of opportunity. There can be many more metrics depending on your data collection process.
The glaring advantage of this model is its accuracy. Nevertheless, this method also requires the most effort from your organization. You need to establish an intricate data input and organization system to ensure you have the metrics on which to base your forecasting on. Fortunately, it can be fully automated. Sophisticated custom CRMs such as Creatio provide opportunity management and lead-scoring features, allowing you to automate sales forecasting while still tailoring it to your business. The reports are generated automatically, so despite this method's complexity, all you need is to put in your data and click a button to generate an error-free report.
Multi-variable forecasting

This approach considers factors that can influence sales performance beyond your own statistics, such as market trends, economic indicators, historical data, marketing efforts, competitor activities, and more.
In other words, multi-variable forecasting adds external factors to your analysis, making your predictions more dependable. It's an excellent model for long-term sales forecasting since it considers factors and opportunities outside your current pipeline. It's a more comprehensive and complex method aiming to consider and weigh various influences on sales. AI-empowered sales automation software can help significantly when applying this method. It can recommend what factors to consider and build prediction models based on internal and external data.
How to Forecast Sales in 7 Steps
The cornerstone of successful sales forecasting is competent data organization and management. To ensure productive sales forecasting, you must establish a robust data culture in your company, utilizing business automation tools that support it. This can be easily done with the help of data management tools such as Creatio CRM, which facilitate input, storage, categorizing, and exchange of customer data.
Now that we've gone through forecasting methods let's figure out how to establish a reliable sales forecasting process that considers your organization's needs.
Step 1: Establish and formalize the sales data management process for your team
This first step is to examine your sales processes and incorporate data management into them. You need to answer the following questions:
- what kinds of metrics do you want to track,
- what system do you want to use for data storage,
- how and when do you log data i.e. what are the protocols and procedures for your sales reps to follow,
- and how do you share it with other team members and departments in the company.
Once you've got the answers, communicate them with your Sales team and other teams that provide you with their data (Marketing, Product, Finance). Establish protocols that facilitate this process and make it easy to follow it for all the employees across the company.
Step 2: Set quotas
Introduce a clear and objective definition of "success" to measure performance accurately. Collaborate with your sales representatives and leaders to define specific sales quotas. These benchmarks will act as financial goals, enabling comparison with your sales forecasts.
Step 3: Choose a sales forecasting method
Now, you can select the sales forecasting method that will suit your needs. Multi-variable forecasting is optimal for the accuracy of your predictions, but if you lack historical data or capacity for complex analytics, go with something simpler. In the latter case, ensure you still track your sales data to switch to a more advanced forecasting model in the future, such as a pipeline or multi-variable method.
Step 4: Select a CRM that supports your sales forecasting
Your organization might already be using Customer Relationship Management software to facilitate sales. However, you need to ensure that it accommodates your sales forecasting processes and can scale up in the future. Powerful data tracking features are necessary for more complicated methodologies. Such features include sales automation, lead scoring, opportunity management, pipeline management, and AI and machine learning analytics tools. Creatio’s CRM also offers automated sales forecasting that enables you to generate forecasts much quicker and with higher accuracy.
Another important CRM feature required for high-level forecasting is integrating data from different departments. You should adopt an enterprise CRM for your whole company and enable data logging from different teams such as Marketing, Service, and Product.
Step 5: Review prior sales forecasts
Analyze previous sales forecasts by comparing them with actual sales figures. You need to identify patterns where forecasts aligned well with existing sales and areas where there were discrepancies. Find the reasons behind any discrepancies — whether they were due to unforeseen market shifts, changes in consumer behavior, or internal factors within the company. You can then use these insights to refine your established sales forecasting process.
Step 6: Keep your sales team informed
Regardless of the sales forecasting method, ensure your sales team stays updated and consistently communicates their feedback. Collect regular feedback from your team on what's effective and what isn't; after all, they understand prospects and overall company sales performance best.
Step 7: Revise your sales forecasting process regularly
What’s important to remember is that sales forecasting is an ongoing process, not a one-off task. Analyze your forecasts for accuracy and tweak the tactics according to your insights. Moreover, regular reviews of your sales forecasting activities will help highlight when you need to switch to a different model or software to scale your operations appropriately to your sales activities.
3 Sales Forecasting Challenges
Even if you carry out all the steps mentioned above perfectly, some external factors can affect the accuracy of your forecast. Knowing how to mitigate these factors and accounting for them in your forecasting is crucial for your organization.
Product lifecycle variability
Product lifecycle variability significantly influences sales forecasting by causing fluctuations in demand, market saturation, inventory management challenges, impacts on marketing strategies, new product introductions, and the need for adaptive sales tactics. Accurate sales forecasting requires a deep understanding of the stage of a product's lifecycle.
Sales team alignment
The lack of sales team alignment jeopardizes the accuracy of your predictions. Transparency and collaboration enhance data quality and enable teams to adjust strategies promptly, leading to more accurate and reliable sales forecasts. Your teams must share information openly and maintain consistent data standards, ensuring everyone is working towards a unified vision.
Uncertain market conditions
Such factors as changing consumer behavior and cautious spending, supply chain disruptions, and discounts introduced by your competitors, can distort sales forecasting by making unreliable predictions. To counter those challenges, you must employ more dynamic forecasting techniques, rely on real-time data, stay updated with market trends, and foster greater collaboration among departments to adjust your strategies early.
How Creatio Sales Makes Sales Forecasting Easy
Creatio Sales is an end-to-end sales management platform that automates your entire sales cycle from lead generation to repeat sales. It includes opportunity management, lead scoring features and sales productivity tools. Creatio’s offers one platform that centralizes your customer data and offers flexible tools and various filters to customize your forecasting models. It enables you to quickly build processes, workflows, and analysis models for your sales team with simple drag-and-drop components.
Creatio offers powerful tools to forecast sales based on various criteria. You can predict sales volumes and revenue based on the sales representatives, accounts, and industries and compare these indicators across periods. You can also create custom forecasts for any data and set up additional indicators, periods, and regions to make your analysis more precise.
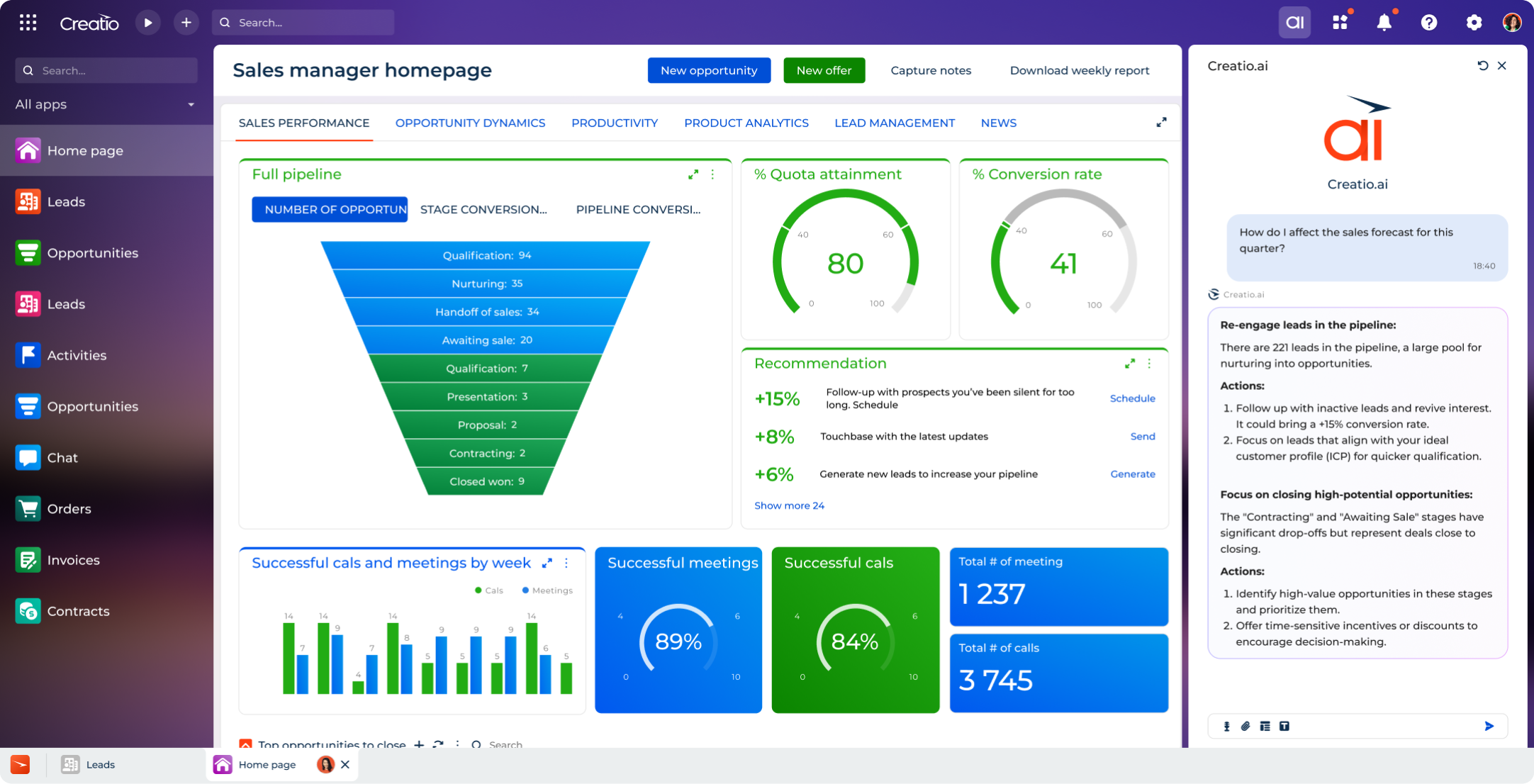
Sales Forecasting in Creatio Sales
Here’s the list of configurations you can implement in your sales forecasting analysis:
- multiple forecasts on any entity – opportunity, order, subscription (incl. monthly, quarterly, annual)
- forecasts by custom sections
- forecast periods (day, week, six months) or use OOTB periods (month, quarter, year)
- forecasts by opportunity amount (can be specified in any currency)
- drill-down entities
- snapshots
- custom rules for calculating metrics
The forecasts are available via multiple dashboards that you can customize for various purposes.
Moreover, Creatio utilizes AI and machine learning technologies to analyze sales data and give you recommendations. You can build and train ML models for predictive data analysis of almost any object based on historical data and your pipeline.
Learn how our client Visiven implemented these features for robust data management and sales forecasting and sign up for a free trial to test-drive Creatio’s comprehensive capabilities.