-
No-Code
Platform
-
Studio
No-code agentic platform delivering the fastest time-to-value and the highest ROI
-
Studio
-
AI-Native CRM
CRM
-
AI-Native CRM
New era CRM to manage customer & operational workflows
CRM Products -
AI-Native CRM
- Industries
- Customers
- Partners
- About
What are Autonomous AI Agents? Boost Business Efficiency with Intelligent Automation
Updated on
January 13, 2026
13 min read
Reduce Manual Effort and Streamline Daily Tasks

Artificial intelligence is rapidly moving beyond chatbots and predictive analytics to a new generation of intelligent tools: autonomous AI agents. Unlike traditional automation systems that follow rigid scripts, autonomous agents can independently make decisions and take action across business processes.
In this article, we’ll explore what autonomous AI agents are, how they can boost efficiency, and why platforms like Creatio make it easier for organizations to unlock their potential without added complexity or cost.
Key Takeaways:
- Autonomous AI agents surpass traditional automation by making informed decisions and taking independent actions.
- They can reduce costs, streamline operations, particularly in high-volume, repetitive tasks, and enhance decision-making.
- Use cases span various industries, including finance, manufacturing, health, and more.
- Deploying autonomous agents presents challenges such as integration complexity, data quality, and governance, but these can be mitigated by platforms that natively embed AI agents.
- The future of autonomous agents is poised to bring multi-agent collaboration, contextual intelligence, and democratized access across all industries.
What are Autonomous AI Agents?
Autonomous AI agents are intelligent software entities capable of performing tasks, making decisions, and taking actions independently – without the need for continuous human input. Unlike traditional automation tools that only follow pre-programmed rules, these agents can act autonomously, adapt to new situations, learn from experiences, and respond to changing conditions in real-time.
Autonomous agents can:
- Analyze data from multiple sources simultaneously
- Make decisions based on business objectives and current conditions
- Take actions across various business processes without human intervention
- Learn and improve their performance over time
- Handle uncertainty and adapt strategies when faced with unexpected situations
What makes autonomous agents truly "autonomous" is their ability to operate independently across entire business workflows – from customer service interactions to financial processing – while maintaining alignment with organizational goals and delivering consistent results.
The State of AI Agents & No-Code
Learn how 560+ leaders across the world use AI and no-code to drive innovation today
How Do Autonomous Agents Work?
Autonomous AI agents work by continuously analyzing data, making decisions, and executing tasks. They perceive and understand information from various sources, formulate a plan of action, make informed decisions based on predefined objectives, and complete tasks without requiring human input for each step. Autonomous agents rely heavily on advanced artificial intelligence technology, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and large language models.
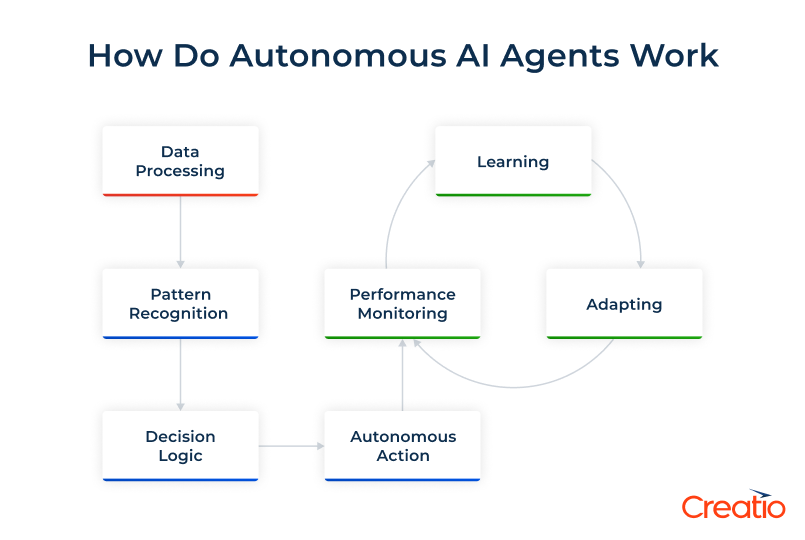
The core autonomous agent capabilities include:
- Data processing – Agents collect and analyze information from CRM systems, databases, market feeds, and external APIs in real-time.
- Pattern recognition – Machine learning algorithms identify trends, anomalies, and opportunities within the collected data.
- Decision logic – Built-in business rules and AI models determine the most appropriate actions based on current conditions.
- Autonomous action execution – AI agents implement solutions, send communications, update records, and trigger workflows across connected systems.
- Performance monitoring – Agents continuously assess their performance based on outcomes and feedback to increase their effectiveness.
The learning component distinguishes autonomous AI agents from traditional automation. They continually evaluate their decision outcomes against key business metrics, including conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. This feedback loop enables AI agents to refine their decision-making processes, adapt to changing market conditions, and become more effective over time without manual reprogramming.
Importantly, autonomous agents still benefit from human in the loop to provide contextual judgment, enforce compliance standards, and guide strategic alignment, ensuring that AI-driven actions remain accurate, ethical, and aligned with organizational goals.
Autonomous Agents vs. AI Agents. What is the Difference?
While the terms "autonomous AI agents" and "AI agents" are often used interchangeably, they represent different levels of artificial intelligence capabilities. All autonomous agents are AI agents, but not all AI agents qualify as truly autonomous.
AI agents are intelligent entities that perform specific tasks using artificial intelligence but may require human guidance, input, or regular supervision.
Common examples include:
- Personal assistants that support humans in performing tasks
- Recommendation engines that suggest products based on algorithms
- Email assistants that categorize and route messages
- Scheduling tools that find meeting times within set parameters
These systems excel within their defined boundaries but require human intervention when encountering scenarios that exceed their initial objective.
Autonomous agents operate as independent business entities capable of managing complete processes from start to finish with minimal human oversight.
Key differences include:
- Proactive behavior - Initiating actions and identifying opportunities independently
- Decision complexity - Handling multi-step processes with competing priorities
- Operational independence - Adapting strategies in real-time to adjust to changing conditions
- Goal setting - Setting up individual goals to achieve larger objectives
The critical distinction between the two lies in their respective responsibilities and scope of work. Traditional AI agents are sophisticated tools that augment human capabilities, while autonomous agents take ownership of business results and manage end-to-end workflows, multi-departmental projects, and strategic initiatives without constant supervision.
Aspect | AI Agents | Autonomous Agents | |
| Definition | Intelligent AI systems that perform specific tasks but may require human guidance or supervision. | Independent systems capable of managing complete processes end-to-end with minimal oversight. | |
| Scope of work | Support humans within defined boundaries; require intervention when tasks exceed parameters. | Own business outcomes; manage workflows, cross-departmental projects, and strategic initiatives. | |
| Proactive behavior | Reactive—respond to input or triggers. | Proactive—initiate actions and identify opportunities independently. | |
| Decision complexity | Handle routine, predefined tasks. | Manage multi-step processes with competing priorities. | |
| Operational independence | Depend on predefined rules and human input. | Adapt strategies in real time to changing conditions. | |
| Goal setting | Execute objectives set by humans. | Define and pursue sub-goals to achieve larger objectives. | |
| Role | Augment human capabilities. | Take ownership of results with minimal supervision. |
Types of Autonomous AI Agents
Autonomous AI agents are categorized based on their ability to adapt, scope of operation, and the complexity of tasks they handle. Understanding these different types helps businesses identify the most suitable solution for their specific requirements and operational challenges.
Main types of autonomous agents include:
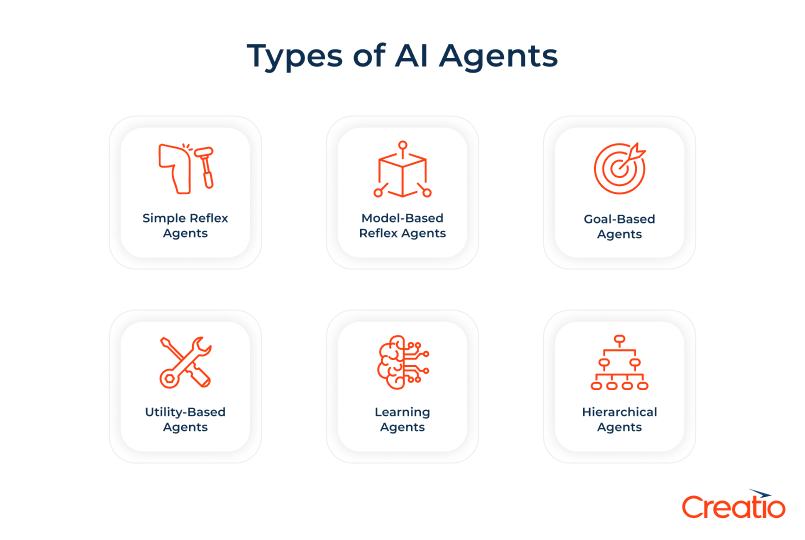
- Simple reflex agents – Act only on the current situation using predefined rules, without retaining memory or learning.
- Model-based agents – Use an internal model of the world to handle partially observable situations and make more informed decisions.
- Goal-based agents – Choose actions by considering how they contribute to achieving specific goals, enabling better planning and flexibility.
- Utility-based agents – Evaluate different outcomes with a utility function and select the action that maximizes overall benefit.
- Learning agents – Improve their performance over time by learning from past experiences and adapting their behavior.
- Hierarchical agents – Organize decision-making into multiple levels (low-level reflexes, mid-level planning, high-level strategy) to manage complex tasks.
Role-based AI agents focus on particular business functions or processes:
- Customer service agents - Handle complete customer interactions from initial contact to issue resolution, manage inquiries across multiple channels, and provide accurate and relevant responses based on customer data.
- Sales and marketing agents - Execute lead qualification, personalized campaigns, and customer relationship nurturing with dynamic audience segmentation.
- Operations management agents - Oversee resource allocation, inventory management, and supply chain coordination while adapting to market disruptions.
Most enterprise deployments use a combination of multiple agent types, forming comprehensive automation ecosystems.
Real-World Examples of Autonomous AI Agents Use Cases
Autonomous agents transform operations across industries by handling complete business processes independently. These real-world implementations demonstrate how organizations achieve measurable results through the strategic deployment of agents.
Financial services
Financial institutions can deploy multiple autonomous AI agents to manage different aspects of their operations, each tailored to handle specific, high-value tasks with speed and precision.
According to Creatio’s The State of AI Agents and No-Code report, 73% business and technology leaders believe AI agents will be critical or important to their organization’s goals in the next 2-3 years
For example, banks can deploy autonomous credit risk management agents that handle the entire loan approval process from application to decision. These agents:
- Independently analyze credit scores
- Verify income documentation
- Assess market conditions
- Evaluate regulatory compliance before making lending decisions
When market conditions shift or new risk patterns emerge, agents automatically adjust their risk models and approval criteria without human intervention.
Financial institutions can also integrate autonomous agents to monitor transaction patterns across multiple channels simultaneously, identify suspicious activities, and implement immediate protective measures.
Upon detecting potential fraud, these autonomous agents can freeze accounts, block transactions, initiate customer verification processes, and notify relevant stakeholders about possible issues. At the same time, they continually refine their detection algorithms based on emerging fraud patterns and analysis of false positives.
Discover more use cases for AI agents in the financial industry
Healthcare operations
Healthcare institutions are leveraging autonomous AI agents to handle patient care, support drug development, and enhance medical diagnosis.
For example, healthcare systems utilize patient care coordination agents that manage entire patient journeys from appointment scheduling to treatment follow-ups. These agents:
- Coordinate between multiple departments
- Automatically adjust scheduling based on patient priorities and resource availability
- Manage medication reminders and refill processes
- Ensure insurance pre-authorizations are completed before procedures
Additionally, integrating AI agents with electronic health records enables continuous monitoring of patient data, identification of potential complications before they become critical, and alerts the appropriate medical staff when necessary. These autonomous agents handle routine medication adjustments, schedule preventive care appointments, and coordinate specialist referrals using patient history and clinical guidelines.
Manufacturing and supply chain
Manufacturing companies can utilize AI agents specifically designed to support their industry, enabling them to predict maintenance needs, enhance product quality, and optimize supply chains.
Manufacturing facilities can deploy predictive maintenance agents that oversee entire maintenance ecosystems, continuously monitoring equipment performance across production lines. When predictive models indicate potential failures, agents can:
- Schedule maintenance windows
- Order replacement parts
- Coordinate technician availability
- Adjust production schedules to minimize disruption
During all these actions, agents also continue to learn from maintenance outcomes to improve prediction accuracy.
Supply chain autonomous agents can also manage complex vendor relationships and inventory decisions across multiple locations. These agents independently adjust order quantities, reroute shipments during disruptions, and optimize inventory levels to ensure optimal supply chain management.
Key Benefits of Autonomous AI Agents
Implementing autonomous agents provides measurable business value across multiple dimensions of a company’s performance. These intelligent entities offer both immediate operational advantages and long-term strategic improvements that compound over time, making them essential for competitive differentiation in a modern business environment.
Operational efficiency and cost reduction
Autonomous agents transform business operations by minimizing manual work, eliminating bottlenecks, and optimizing resource utilization across the organization. Because AI agents operate continuously, without breaks, holidays, or sick days, they deliver consistent service levels and reduce operational overhead.
According to a recent study conducted by Creatio, over 80% of business and technology leaders view AI agents as a means to drive productivity, create growth opportunities for existing staff, or create new roles within the organization.
Key operational advantages of autonomous agents include:
- 24/7 availability with performance consistency, allowing for round-the-clock process management and customer service operations
- Scalable operations capable of handling growing operations without proportional growth of infrastructure or staffing costs
- Error reduction achieved using consistent application of business rules and automated quality checks
- Process optimization from identifying inefficiencies and automatically implementing necessary improvements or fixes
- Resource allocation improves productivity and minimizes waste
- Faster response times when it comes to internal requests, system issues, and customer inquiries
Additionally, autonomous AI agents reduce costs by handling high-volume, repetitive tasks, such as data entry, transaction processing, and customer support. They operate continuously, scale on demand, and minimize errors—cutting expenses while boosting efficiency.
Autonomous agents also relieve human employees of many low-level tasks, opening more time for strategic, creative, and relationship-building activities that drive better business value.
Enhanced decision-making and strategic advantage
Beyond operational efficiency, autonomous agents also provide competitive intelligence and strategic insights, enabling superior decision-making capabilities. They continuously analyze market conditions, customer behavior, and operational performance to identify opportunities and risks that human overseers might miss.
Notable strategic benefits of autonomous agents are:
- Data-driven insights based on continuous analysis of business metrics, market trends, and customer behavior patterns
- Predictive capabilities anticipate market changes, customer needs, and various operational challenges before they have an impact on business performance
- Competitive advantages such as faster market response and increased agility in business operations
- Risk mitigation is enabled by the ability to identify potential problems early on and implement preventive measures without requiring human input
- Market responsiveness with real-time adjustments to marketing strategies, pricing, and inventory depending on current conditions
Long-term strategic value strengthens as autonomous agents evolve, acquire institutional knowledge, and enhance decision-making capabilities over time. Organizations benefit from this compounding learning effect, with agents becoming increasingly valuable business assets that develop a deeper understanding of industry dynamics, customer preferences, and optimal operational strategies that could have taken years to develop in human-only teams.
Challenges and Risks of Deploying Autonomous Agents
While autonomous agents deliver significant benefits, organizations must carefully navigate implementation complexities and operational risks to achieve successful deployment. Understanding these challenges enables better planning, resource allocation, and risk mitigation strategies.
According to a Creatio survey of over 560 business and technology leaders, the top barriers to broader AI agent adoption include data quality and system integration challenges (51%), regulatory and security concerns (43%), and limited training and enablement (34%).
Here’s a breakdown of key challenges and risks:
- System integration complexity requires extensive API development and middleware configuration to connect with legacy systems and existing infrastructure
- Data quality requirements demand clean, structured, and accessible data across multiple business systems for effective agent operation and decision-making
- High implementation costs with projects typically requiring multiple months and substantial expenses that often exceed initial estimates due to unforeseen technical requirements
- Employee resistance and change management concerns about job displacement necessitate comprehensive training programs and clear communication strategies
- Over-reliance on automation that reduces human expertise and creates vulnerabilities when AI agents encounter unexpected scenarios or system failures
- Security and compliance risks, including potential data breaches, regulatory oversight requirements, and maintaining audit trails for automated decisions
- Governance and accountability challenges when determining responsibility for autonomous agent decisions and actions that impact business outcomes
- Vendor dependence risks when using third-party platforms that can unexpectedly increase pricing, change features, and modify the availability of critical business automation
- Performance monitoring complexity requires robust frameworks to ensure agents operate within acceptable parameters while maintaining business objective alignment
Addressing these challenges requires choosing the right vendor.
Unlike legacy solutions that bolt agents onto complex architectures or create silos across business functions, platforms like Creatio natively embed autonomous AI agents at no additional cost.
This eliminates the need for heavy integration work, reduces total implementation expenses, and ensures agents operate seamlessly across systems and processes. By removing architectural complexity and avoiding hidden licensing costs, businesses can accelerate adoption, reduce risk, and focus on capturing value from AI agents without the usual barriers.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Autonomous AI Agents
The future of autonomous AI agents is poised for deeper integration, greater sophistication, and widespread adoption across various industries. As technology advances, these agents gain more advanced reasoning capabilities and evolve beyond task automation to become collaborative digital colleagues that work alongside humans in decision-making, innovation, and strategic execution.
One key trend is the rise of multi-agent systems, where autonomous agents interact with each other to coordinate complex workflows. Instead of operating in isolation, agents in the multi-agent framework will communicate, negotiate, and collaborate with other agents to optimize outcomes across entire organizations or even between enterprises. This opens the door to self-organizing supply chains, adaptive financial systems, and dynamic service delivery models.
Another critical direction is contextual intelligence. Future agents will increasingly combine structured business data with unstructured inputs, such as natural language, video, and sensor streams. This will allow them to understand context, anticipate needs, and take proactive action rather than simply responding to predefined triggers.
Finally, autonomous agents will become more accessible and democratized. With vendors embedding agents directly into enterprise platforms, businesses of all sizes will be able to leverage their capabilities without massive upfront investment or complex integration projects.
Autonomous AI Agents in Action with Creatio
Creatio represents a new paradigm in autonomous AI implementation, delivering an agentic CRM and workflow platform with no-code and AI at its core that embeds intelligent agents directly into business operations.
Instead of treating Artificial Intelligence as an add-on, Creatio natively integrates agentic, predictive, and generative AI into its core architecture, enabling the deployment of autonomous agents that can understand every data object, relationship, and workflow. The conversational interface of the platform enables users to simply describe their needs in natural language, and the system automatically deploys appropriate agents to execute tasks, surface insights, and provide recommendations.
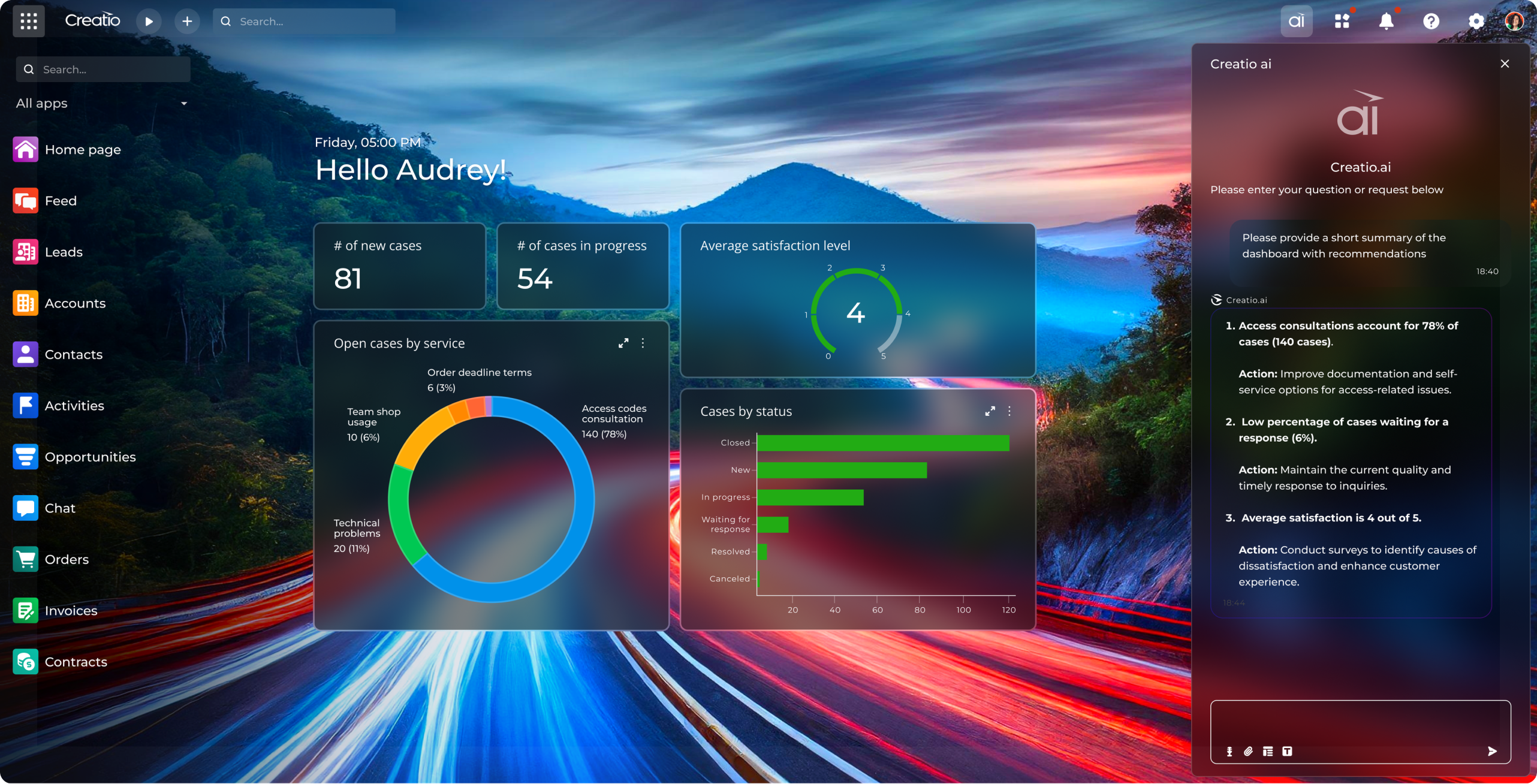
Creatio delivers purpose-built autonomous agents designed for highly specific industries and business functions. Users can choose from a variety of out-of-the-box agents or build custom agents using natural language and advanced no-code capabilities, which require no technical expertise. The platform includes role-based agents for sales, marketing, and customer service teams, each embedded with deep industry-specific knowledge, enabling immediate autonomous operation. The Financial Services Agent exemplifies this approach, offering powerful agentic AI capabilities and ready-to-use financial workflows that are pre-trained, fully integrated, and require no technical customization to start delivering results.
Creatio prioritizes enterprise-grade security, strong AI governance, and a human-in-the-loop approach to ensure responsible adoption. It safeguards sensitive data, ensures transparency and accountability, and keeps AI outcomes aligned with policies and regulations—enabling organizations to deploy autonomous agents with confidence.
All autonomous AI capabilities are included in Creatio’s core platform pricing with no additional fees for AI features. This transparent approach enables businesses to confidently expand AI adoption while maintaining predictable and sustainable budgets.
Summary
Autonomous agents represent a significant shift in business automation, transitioning from task execution to intelligent systems that manage entire workflows independently. They enable organizations to scale decision-making and efficiency to new levels.
From finance to healthcare, early adopters are already seeing how these autonomous agents enhance human capabilities and drive operational excellence. Success, however, depends on selecting the right vendor, seamlessly connecting with existing systems, and having a clear strategy for human–AI collaboration.
The future will belong to businesses that pair human agents' creativity and strategic thinking with AI-powered automation. Autonomous agents are not replacing people, but augmenting them—freeing teams to focus on high-value work while AI handles routine processes reliably and efficiently. Those who embrace this shift early will gain lasting competitive advantages in agility, customer experience, and resource optimization.






















































